Differential requirements for Alix and ESCRT-III in cytokinesis and HIV-1 release
- PMID: 18641129
- PMCID: PMC2492449
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0802008105
Differential requirements for Alix and ESCRT-III in cytokinesis and HIV-1 release
Abstract
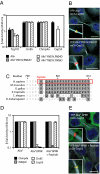
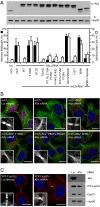
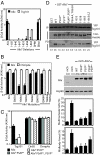
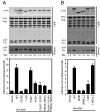
The ESCRT machinery functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, namely multivesicular body formation, the terminal stages of cytokinesis and HIV-1 release. Here, we show that the ESCRT-III-binding protein Alix is recruited to the midbody of dividing cells through binding Cep55 via an evolutionarily conserved peptide. Disruption of Cep55/Alix/ESCRT-III interactions causes formation of aberrant midbodies and cytokinetic failure, demonstrating an essential role for these proteins in midbody morphology and cell division. We also show that the C terminus of Alix encodes a multimerization activity that is essential for its function in Alix-dependent HIV-1 release and for interaction with Tsg101. Last, we demonstrate that overexpression of Chmp4b and Chmp4c differentially inhibits HIV-1 release and cytokinesis, suggesting possible reasons for gene expansion within the mammalian Class E VPS pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Glotzer M. Animal cell cytokinesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:351–386. - PubMed
-
- Eggert US, Mitchison TJ, Field CM. Animal cytokinesis: From parts list to mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:543–566. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Gruneberg U. Cytokinesis: Placing and making the final cut. Cell. 2007;131:847–860. - PubMed
-
- Fabbro M, et al. Cdk1/Erk2- and Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of a centrosome protein, Cep55, is required for its recruitment to midbody and cytokinesis. Dev Cell. 2005;9:477–488. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Garay I, Rustom A, Gerdes HH, Kutsche K. The novel centrosomal associated protein CEP55 is present in the spindle midzone and the midbody. Genomics. 2006;87:243–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

