Bcl-xL and UVRAG cause a monomer-dimer switch in Beclin1
- PMID: 18641390
- PMCID: PMC3258859
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M804723200
Bcl-xL and UVRAG cause a monomer-dimer switch in Beclin1
Abstract
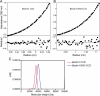
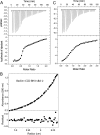
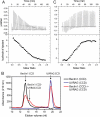
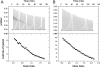
Beclin1 has a key regulatory role in the initiation of autophagy and is a tumor suppressor. We have examined the interplay between viral or human Bcl-2-like proteins and UVRAG and their opposite effects on Beclin1. We show that Beclin1 forms a dimer in solution via its coiled-coil domain both in vivo and in vitro. Viral Bcl-2 binds independently to two sites on the Beclin1 dimer, one with high affinity and one with lower affinity, whereas human Bcl-x(L) binds both sites equally with relatively low affinity. UVRAG disrupts the Beclin1-dimer interface, forming a heterodimer with Beclin1, suggesting that this is how UVRAG causes its effects on Beclin1 to activate autophagy. Both Bcl-2-like proteins reduce the affinity of UVRAG for Beclin1 approximately 4-fold, suggesting that they stabilize the Beclin1 dimer. Moreover, coimmunoprecipitation assays show that UVRAG substantially reduces Beclin1 dimerization in vivo. These data explain the concentration-dependent interplay between Bcl-2, UVRAG, and Beclin1, as both tumor suppressors, UVRAG and Beclin1, have single-copy mutations in human cancers. Furthermore, our data suggest that an alternative strategy for developing anti-cancer compounds would be to disrupt the Beclin1-dimer interface.
Figures

References
-
- Levine, B., and Klionsky, D. J. (2004) Dev. Cell 6 463-477 - PubMed
-
- Shimizu, S., Kanaseki, T., Mizushima, N., Mizuta, T., Arakawa-Kobayashi, S., Thompson, C. B., and Tsujimoto, Y. (2004) Nat. Cell Biol. 6 1221-1228 - PubMed
-
- Yu, L., Alva, A., Su, H., Dutt, P., Freundt, E., Welsh, S., Baehrecke, E. H., and Lenardo, M. J. (2004) Science 304 1500-1502 - PubMed
-
- Aita, V. M., Liang, X. H., Murty, V. V., Pincus, D. L., Yu, W., Cayanis, E., Kalachikov, S., Gilliam, T. C., and Levine, B. (1999) Genomics 59 59-65 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

