Actin restricts FcepsilonRI diffusion and facilitates antigen-induced receptor immobilization
- PMID: 18641640
- PMCID: PMC3022440
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1755
Actin restricts FcepsilonRI diffusion and facilitates antigen-induced receptor immobilization
Abstract
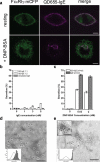
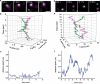
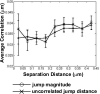
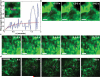
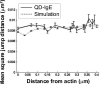
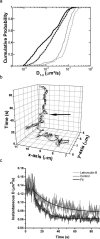
The actin cytoskeleton has been implicated in restricting diffusion of plasma membrane components. Here, simultaneous observations of quantum dot-labelled FcepsilonRI motion and GFP-tagged actin dynamics provide direct evidence that actin filament bundles define micron-sized domains that confine mobile receptors. Dynamic reorganization of actin structures occurs over seconds, making the location and dimensions of actin-defined domains time-dependent. Multiple FcepsilonRI often maintain extended close proximity without detectable correlated motion, suggesting that they are co-confined within membrane domains. FcepsilonRI signalling is activated by crosslinking with multivalent antigen. We show that receptors become immobilized within seconds of crosslinking. Disruption of the actin cytoskeleton results in delayed immobilization kinetics and increased diffusion of crosslinked clusters. These results implicate actin in membrane partitioning that not only restricts diffusion of membrane proteins, but also dynamically influences their long-range mobility, sequestration and response to ligand binding.
Figures
References
-
- Dustin ML, Cooper JA. The immunological synapse and the actin cytoskeleton: molecular hardware for T cell signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2000;1:23–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, et al. Characterizing the topography of membrane receptors and signaling molecules from spatial patterns obtained using nanometer-scale electron-dense probes and electron microscopy. Micron. 2006;1:14–34. - PubMed
-
- Boniface JJ, et al. Initiation of signal transduction through the T cell receptor requires the multivalent engagement of peptide/MHC ligands [corrected]. Immunity. 1998;4:459–66. - PubMed
-
- Kraft S, Kinet JP. New developments in FcepsilonRI regulation, function and inhibition. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007;5:365–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 GM 67594/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR022493/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM067597/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR11830/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR16918/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019287/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051575/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AO051575/AO/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM067594/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM049814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR022493/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA118100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR19287/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM49814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR14668/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR15734/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

