Assessment of tissue redox status using metabolic responsive contrast agents and magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 18644197
- PMCID: PMC2752670
- DOI: 10.1211/jpp.60.8.0011
Assessment of tissue redox status using metabolic responsive contrast agents and magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
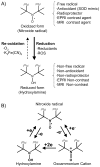
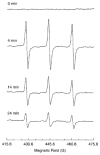
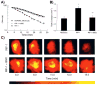
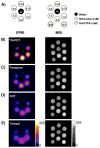
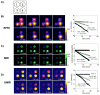
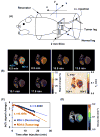
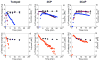
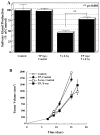
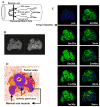
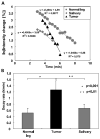
Regulation of tissue redox status is important to maintain normal physiological conditions in the living body. Disruption of redox homoeostasis may lead to oxidative stress and can induce many pathological conditions such as cancer, neurological disorders and ageing. Therefore, imaging of tissue redox status could have clinical applications. Redox imaging employing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with nitroxides as cell-permeable redox-sensitive contrast agents has been used for non-invasive monitoring of tissue redox status in animal models. The redox imaging applications of nitroxide electron paramagnetic resonance imaging (EPRI) and MRI are reviewed here, with a focus on application of tumour redox status monitoring. While particular emphasis has been placed on differences in the redox status in tumours compared to selected normal tissues, the technique possesses the potential to have broad applications to the study of other disease states, inflammatory processes and other circumstances where oxidative stress is implicated.
Figures
References
-
- Barbier EL, Lamalle L, Decorps M. Methodology of brain perfusion imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13:496–520. - PubMed
-
- Berliner JL, Fujii H. Magnetic resonance imaging of biological specimens by electron paramagnetic resonance of nitroxide spin labels. Science. 1985;227:517–9. - PubMed
-
- Berliner LJ, Fujii H, Wan XM, Lukiewicz SJ. Feasibility study of imaging a living murine tumor by electron paramagnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med. 1987;4:380–4. - PubMed
-
- Brasch RC. Work in progress: methods of contrast enhancement for NMR imaging and potential applications. A subject review. Radiology. 1983;147:781–8. - PubMed
-
- Brasch RC, London DA, Wesbey GE, Tozer TN, Nitecki DE, Williams RD, Doemeny J, Tuck LD, Lallemand DP. Work in progress: nuclear magnetic resonance study of a paramagnetic nitroxide contrast agent for enhancement of renal structures in experimental animals. Radiology. 1983;147:773–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

