EGFR activation confers protections against UV-induced apoptosis in cultured mouse skin dendritic cells
- PMID: 18644433
- PMCID: PMC2614344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.06.010
EGFR activation confers protections against UV-induced apoptosis in cultured mouse skin dendritic cells
Erratum in
- Cell Signal. 2009 Feb;21(2):365
Abstract
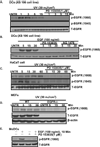
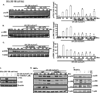
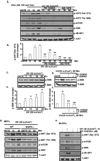
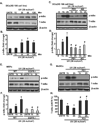
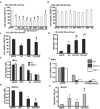
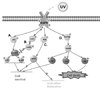
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) induces apoptosis and functional maturation in skin dendritic cells (DCs). However, the molecular mechanisms through which UV activates DCs have not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, we examined the mechanisms of activation and apoptosis of DCs after UV irradiation by focusing on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Our previous studies have demonstrated that in addition to cognate ligands, EGFR is also activated by UVB irradiation in cultured human skin keratinocytes in vitro and in human skin in vivo. We found for the first time in this study that UV also induces EGFR activation in cultured mouse skin DCs (XS 106 cell line) as well as mouse monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs). Pharmacological inhibition of EGFR tyrosine kinase significantly inhibits UV-induced ERK, p38, and JNK MAP kinases, and their effectors, transcription factors c-Fos and c-Jun. Inhibition of EGFR also suppresses UV-induced activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways. Our data demonstrated that UV induces LKB1/AMPK pathway, also dependent on EGFR trans-activation. We further observed that MAPK, LKB1/AMPK, PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K as well as NF-kappaB activation are impaired in EGFR-/- cells compared to wide type MEF cells after UV radiation. Taken together, we conclude that UV induces multiple signaling pathways mediated by EGFR trans-activation leading to possible maturation, apoptosis and survival, and EGFR activation protects against UV-induced apoptosis in cultured mouse dendritic cells.
Figures

References
-
- Ruderman NB, Keller C, Richard AM, Saha AK, Luo Z, Xiang X, Giralt M, Ritov VB, Menshikova EV, Kelley DE, Hidalgo J, Pedersen BK, Kelly M. Diabetes. 2006;55 Suppl 2:S48–S54. - PubMed
-
- Meunier L, Eur J. Dermatol. 1999;9(4):269–275. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa S, Ohtani T, Mizuashi M, Mollah ZU, Ito Y, Tagami H, Aiba S. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123(2):361–370. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang L, Wang B, Shinder GA, Shivji GM, Mak TW, Sauder DN. J Immunol. 1999;162(3):1440–1447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

