Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates SNARE-dependent membrane fusion
- PMID: 18644890
- PMCID: PMC2483516
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200801056
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates SNARE-dependent membrane fusion
Abstract
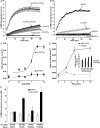
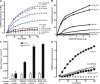
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI 4,5-P(2)) on the plasma membrane is essential for vesicle exocytosis but its role in membrane fusion has not been determined. Here, we quantify the concentration of PI 4,5-P(2) as approximately 6 mol% in the cytoplasmic leaflet of plasma membrane microdomains at sites of docked vesicles. At this concentration of PI 4,5-P(2) soluble NSF attachment protein receptor (SNARE)-dependent liposome fusion is inhibited. Inhibition by PI 4,5-P(2) likely results from its intrinsic positive curvature-promoting properties that inhibit formation of high negative curvature membrane fusion intermediates. Mutation of juxtamembrane basic residues in the plasma membrane SNARE syntaxin-1 increase inhibition by PI 4,5-P(2), suggesting that syntaxin sequesters PI 4,5-P(2) to alleviate inhibition. To define an essential rather than inhibitory role for PI 4,5-P(2), we test a PI 4,5-P(2)-binding priming factor required for vesicle exocytosis. Ca(2+)-dependent activator protein for secretion promotes increased rates of SNARE-dependent fusion that are PI 4,5-P(2) dependent. These results indicate that PI 4,5-P(2) regulates fusion both as a fusion restraint that syntaxin-1 alleviates and as an essential cofactor that recruits protein priming factors to facilitate SNARE-dependent fusion.
Figures


References
-
- Aoyagi, K., T. Sugaya, M. Umeda, S. Yamamoto, S. Terakawa, and M. Takahashi. 2005. The activation of exocytotic sites by the formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate microdomains at syntaxin clusters. J. Biol. Chem. 280:17346–17352. - PubMed
-
- Bai, J., W.C. Tucker, and E.R. Chapman. 2004. PIP2 increases the speed of response of synaptotagmin and steers its membrane-penetration activity toward the plasma membrane. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11:36–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

