Selection and persistence of CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli in the intestinal flora of pigs treated with amoxicillin, ceftiofur, or cefquinome
- PMID: 18644956
- PMCID: PMC2565910
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00354-08
Selection and persistence of CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli in the intestinal flora of pigs treated with amoxicillin, ceftiofur, or cefquinome
Abstract
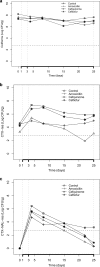
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), mainly of the CTX-M family, have been associated with Escherichia coli strains of animal origin in Europe. An in vivo experiment was performed to study the effects of veterinary beta-lactam drugs on the selection and persistence of ESBL-producing E. coli in the intestinal flora of pigs. Twenty pigs were randomly allocated into three treatment groups and one control group. All pigs were inoculated intragastrically with 10(10) CFU of a nalidixic acid (NAL)-resistant mutant derived from a CTX-M-1-producing E. coli strain of pig origin. Treatment with amoxicillin, ceftiofur, or cefquinome according to the instructions on the product label was initiated immediately after bacterial inoculation. Feces were collected from the rectum before inoculation and on days 4, 8, 15, 22, and 25 after the start of treatment. The total and resistant coliforms were counted on MacConkey agar with and without cefotaxime (CTX). Furthermore, MacConkey agar with CTX and NAL was used to count the number of CFU of the inoculated strain. Significantly higher counts of CTX-resistant coliforms were observed in the three treatment groups than in the control group for up to 22 days after the discontinuation of treatment. Ceftiofur and cefquinome exerted larger selective effects than amoxicillin, and the effects persisted beyond the withdrawal times recommended for these cephalosporins. The inoculated strain was detected in only nine animals on day 25. The increase in the number of CTX-resistant coliforms was mainly due to the proliferation of indigenous CTX-M-producing strains and the possible emergence of strains that acquired CTX-M genes by horizontal transfer. The study provides evidence that the cephalosporins used in pig production select for CTX-M-producing E. coli strains. Their use in animals should be carefully considered in view of the critical importance of cephalosporins and the zoonotic potential of ESBL-producing bacteria.
Figures
References
-
- Aarestrup, F. M., H. Hasman, Y. Agerso, L. B. Jensen, S. Harksen, and B. Svensmark. 2006. First description of blaCTX-M-1-carrying Escherichia coli isolates in Danish primary food production. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 57:1258-1259. - PubMed
-
- Burch, D., C. Duran, and F. M. Aarestrup. 2008. Guidelines for antimicrobial use in swine p. 102-125. In L. Guardabassi, L. Jensen, and H. Kruse (ed.), Guide to antimicrobial use in animals. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, United Kingdom.
-
- Canton, R., and T. M. Coque. 2006. The CTX-M beta-lactamase pandemic. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9:466-475. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2004. One-day (24-28 h) standardized laboratory protocol for molecular subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, non-typhoidal Salmonella serotypes, and Shigella sonnei by pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). PulseNet manual. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

