The pak4 protein kinase plays a key role in cell survival and tumorigenesis in athymic mice
- PMID: 18644984
- PMCID: PMC2822623
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0087
The pak4 protein kinase plays a key role in cell survival and tumorigenesis in athymic mice
Abstract
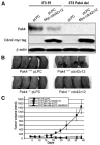
Pak4 is a member of the B group of p21-activated (Pak) kinases, originally identified as an effector protein for Cdc42. Although Pak4 is expressed at low levels in most adult tissues, it is highly overexpressed in tumor cell lines. Here, we show that Pak4 is also overexpressed in primary tumors, including colon, esophageal, and mammary tumors. Overexpression of Pak4 also leads to tumor formation in athymic mice, whereas deletion of Pak4 inhibits tumorigenesis. Although a constitutively active Pak4 mutant was previously shown to promote oncogenic transformation in cultured cells, our results are the first to show that Pak4 also promotes tumorigenesis in experimental animals. Furthermore, these results show for the first time that not only constitutively active Pak4, but also wild-type Pak4, is transforming, when experimental animals are used. These results are highly significant because wild-type Pak4, rather than activated Pak4, is overexpressed in tumor cells. Our results suggest that overexpression or activation of Pak4 is a key step in oncogenic transformation, due to its ability to promote cell survival and subsequent uncontrolled proliferation. The finding that Pak4 is up-regulated in so many types of cancers indicates that Pak4 may play a vital role in a wide range of different types of cancer. This makes it an attractive candidate for drug therapy for different types of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
The protein kinase Pak4 disrupts mammary acinar architecture and promotes mammary tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2010 Nov 4;29(44):5883-94. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.329. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20697354 Free PMC article.
-
The serine/threonine kinase PAK4 prevents caspase activation and protects cells from apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 27;276(17):14414-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011046200. Epub 2001 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278822
-
Knockdown of PAK4 or PAK1 inhibits the proliferation of mutant KRAS colon cancer cells independently of RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Feb;11(2):109-21. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0466. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23233484
-
The role of PAK4 in the immune system and its potential implication in cancer immunotherapy.Cell Immunol. 2021 Sep;367:104408. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104408. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Cell Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34246086 Review.
-
Why is PAK4 overexpressed in cancer?Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021 Sep;138:106041. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106041. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34274498 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse models of PAK function.Cell Logist. 2012 Apr 1;2(2):84-88. doi: 10.4161/cl.21381. Cell Logist. 2012. PMID: 23162740 Free PMC article.
-
PAK4: a pluripotent kinase that regulates prostate cancer cell adhesion.J Cell Sci. 2010 May 15;123(Pt 10):1663-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.055707. Epub 2010 Apr 20. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20406887 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Cdc42 in cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Nov;17(11):1263-73. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.828037. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23957315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proximity proteomics identifies PAK4 as a component of Afadin-Nectin junctions.Nat Commun. 2021 Sep 7;12(1):5315. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25011-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34493720 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PAK4 Inhibits Ras-Mediated Signaling and Multiple Oncogenic Pathways in High-Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma.Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;81(1):199-212. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0854. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33168646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daniels RH, Bokoch GM. p21-Activated protein kinase: a crucial component of morphological signaling? Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:350–5. - PubMed
-
- Knaus UG, Bokoch GM. The p21Rac/Cdc42-activated kinases (PAKs) Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;30:857–62. - PubMed
-
- Sells MA, Chernoff J. Emerging from the Pak: the p21-activated protein kinase family. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;7:162–7. - PubMed
-
- Jaffer ZM, Chernoff J. p21-Activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34:713–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

