WT1 induction of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3 represents a novel mechanism of growth suppression
- PMID: 18644985
- PMCID: PMC2587040
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0078
WT1 induction of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3 represents a novel mechanism of growth suppression
Abstract
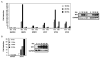
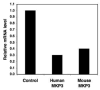
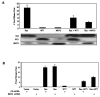
In its role as a tumor suppressor, WT1 transactivates several genes that are regulators of cell growth and differentiation pathways. For instance, WT1 induces the expression of the cell cycle regulator p21, the growth-regulating glycoprotein amphiregulin, the proapoptotic gene Bak, and the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor Sprouty1. Here, we show that WT1 transactivates another important negative regulator of the Ras/MAPK pathway, MAPK phosphatase 3 (MKP3). In a WT1-inducible cell line that exhibits decreased cell growth and increased apoptosis on expression of WT1, microarray analysis showed that MKP3 is the most highly induced gene. This was confirmed by real-time PCR where MKP3 and other members of the fibroblast growth factor 8 syn expression group, which includes Sprouty 1 and the Ets family of transcription factors, were induced rapidly following WT1 expression. WT1 induction was associated with a block in the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation, an effect mediated by MKP3. In the presence of a dominant-negative MKP3, WT1 could no longer block phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Lastly, when MKP3 expression is down-regulated by short hairpin RNA, WT1 is less able to block Ras-mediated transformation of 3T3 cells.
Figures


References
-
- Rivera MN, Haber DA. Wilms' tumour: connecting tumorigenesis and organ development in the kidney. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:699–712. - PubMed
-
- Hosono S, Gross I, English MA, et al. E-cadherin is a WT1 target gene. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10943–53. - PubMed
-
- Lee SB, Huang K, Palmer R, et al. The Wilms tumor suppressor WT1 encodes a transcriptional activator of amphiregulin. Cell. 1999;98:663–73. - PubMed
-
- English MA, Licht JD. Tumor-associated WT1 missense mutants indicate that transcriptional activation by WT1 is critical for growth control. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13258–63. - PubMed
-
- Palmer RE, Kotsianti A, Cadman B, et al. WT1 regulates the expression of the major glomerular podocyte membrane protein Podocalyxin. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1805–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

