Destabilization of ERBB2 transcripts by targeting 3' untranslated region messenger RNA associated HuR and histone deacetylase-6
- PMID: 18644987
- PMCID: PMC2583372
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2110
Destabilization of ERBB2 transcripts by targeting 3' untranslated region messenger RNA associated HuR and histone deacetylase-6
Abstract
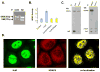
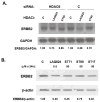
In addition to repressing ERBB2 promoter function, histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors induce the accelerated decay of mature ERBB2 transcripts; the mechanism mediating this transcript destabilization is unknown but depends on the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of ERBB2 mRNA. Using ERBB2-overexpressing human breast cancer cells (SKBR3), the mRNA stability factor HuR was shown to support ERBB2 transcript integrity, bind and endogenously associate with a conserved U-rich element within the ERBB2 transcript 3' UTR, coimmunoprecipitate with RNA-associated HDAC activity, and colocalize with HDAC6. HDAC6 also coimmunoprecipitates with HuR in an RNA-dependent manner and within 6 hours of exposure to a pan-HDAC inhibitor dose, that does not significantly alter cytosolic HuR levels or HuR binding to ERBB2 mRNA. Cellular ERBB2 transcript levels decline while remaining physically associated with HDAC6. Knockdown of HDAC6 protein by small interfering RNA partially suppressed the ERBB2 transcript decay induced by either pan-HDAC or HDAC6-selective enzymatic inhibitors. Three novel hydroxamates, ST71, ST17, and ST80 were synthesized and shown to inhibit HDAC6 with 14-fold to 31-fold greater selectivity over their binding and inhibition of HDAC1. Unlike more potent pan-HDAC inhibitors, these HDAC6-selective inhibitors produced dose-dependent growth arrest of ERBB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells by accelerating the decay of mature ERBB2 mRNA without repressing ERBB2 promoter function. In sum, these findings point to the therapeutic potential of HuR and HDAC6-selective inhibitors, contrasting ERBB2 stability effects induced by HDAC6 enzymatic inhibition and HDAC6 protein knockdown, and show that ERBB2 transcript stability mechanisms include exploitable targets for the development of novel anticancer therapies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of ERBB2 by miR26a/b and HuR confers resistance to tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 18;292(33):13551-13564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780973. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28637868 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional repression of ErbB2 by histone deacetylase inhibitors detected by a genomically integrated ErbB2 promoter-reporting cell screen.Mol Cancer Ther. 2002 Apr;1(6):385-92. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002. PMID: 12477051
-
Enhanced pharmacodynamic and antitumor properties of a histone deacetylase inhibitor encapsulated in liposomes or ErbB2-targeted immunoliposomes.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 May 1;11(9):3392-401. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2445. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15867240
-
Trichostatin-A modulates claudin-1 mRNA stability through the modulation of Hu antigen R and tristetraprolin in colon cancer cells.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2610-21. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt207. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23880304 Free PMC article.
-
Explorative study on isoform-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009 Sep;57(9):897-906. doi: 10.1248/cpb.57.897. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009. PMID: 19721249 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of PADI2 as a potential breast cancer biomarker and therapeutic target.BMC Cancer. 2012 Oct 30;12:500. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-500. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23110523 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with P-gp, HER-2 positivity, and poor outcome in breast cancer.Tumour Biol. 2013 Aug;34(4):2299-308. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0774-3. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23605320
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of ERBB2 by miR26a/b and HuR confers resistance to tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 18;292(33):13551-13564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780973. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28637868 Free PMC article.
-
Current Evidence and Future Perspectives on HuR and Breast Cancer Development, Prognosis, and Treatment.Neoplasia. 2016 Nov;18(11):674-688. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Neoplasia. 2016. PMID: 27764700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC inhibitors induce transcriptional repression of high copy number genes in breast cancer through elongation blockade.Oncogene. 2013 Jun 6;32(23):2828-35. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.32. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23435418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scott GK, Marden C, Xu F, Kirk L, Benz CC. Transcriptional repression of ErbB2 by histone deacetylase inhibitors detected by a genomically integrated ErbB2 promoter-reporting cell screen. Mol Cancer Therapeutics. 2002;1:385–392. - PubMed
-
- Marx C, Berger C, Xu F, Amend C, Scott GK, Hann B, Park JW, Benz CC. Validated high-throughput screening of drug-like small molecules for inhibitors of ErbB2 transcription. ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies. 2006;4:273–284. - PubMed
-
- Drummond DC, Noble CO, Kirpotin DB, Guo Z, Scott GK, Benz CC. Clinical development of histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:495–528. - PubMed
-
- Drummond DC, Marx C, Guo Z, Scott G, Noble C, Wang D, Pallavicini M, Park JW, Kirpotin DB, Benz CC. Enhanced pharmacodynamic and antitumor properties of a histone deacetylase inhibitor encapsulated in liposomes or ErbB2-targeted immunoliposomes. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3392–3401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

