Prostate-specific membrane antigen associates with anaphase-promoting complex and induces chromosomal instability
- PMID: 18645024
- PMCID: PMC2548318
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0005
Prostate-specific membrane antigen associates with anaphase-promoting complex and induces chromosomal instability
Erratum in
- Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Sep;7(9):3122. Ryazantsev, Sergey [added]
Abstract
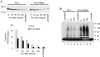
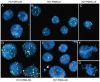
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is a transmembrane protein highly expressed in advanced and metastatic prostate cancers. The pathologic consequence of elevated PSMA expression in not known. Here, we report that PSMA is localized to a membrane compartment in the vicinity of mitotic spindle poles and associates with the anaphase-promoting complex (APC). PSMA-expressing cells prematurely degrade cyclin B and exit mitosis due to increased APC activity and incomplete inactivation of APC by the spindle assembly checkpoint. Further, expression of PSMA in a karyotypically stable cell line induces aneuploidy. Thus, these findings provide the first evidence that PSMA has a causal role in the induction of aneuploidy and might play an etiologic role in the progression of prostate cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A specific form of phospho protein phosphatase 2 regulates anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome association with spindle poles.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 15;21(6):897-904. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0598. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20089842 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex by the Xnf7 ubiquitin ligase.J Cell Biol. 2005 Apr 11;169(1):61-71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200411056. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15824132 Free PMC article.
-
ATP is required for the release of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome from inhibition by the mitotic checkpoint.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 23;107(12):5351-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001875107. Epub 2010 Mar 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20212161 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin A and Nek2A: APC/C-Cdc20 substrates invisible to the mitotic spindle checkpoint.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):72-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0380072. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074038 Review.
-
Non-mitotic functions of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):572-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21439391 Review.
Cited by
-
CART cell therapy for prostate cancer: status and promise.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jan 3;12:391-395. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S185556. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30655675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Nuclear Medicine in Prostate Cancer: Current State and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;15(19):4746. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194746. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in primary staging of prostate carcinoma: preliminary results on differences between black and white South-Africans.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018 Feb;45(2):226-234. doi: 10.1007/s00259-017-3852-8. Epub 2017 Nov 4. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29101444 Free PMC article.
-
Dimeric DNA Aptamer Complexes for High-capacity-targeted Drug Delivery Using pH-sensitive Covalent Linkages.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013 Jul 16;2(7):e107. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2013.37. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013. PMID: 23860551 Free PMC article.
-
Auger Radiopharmaceutical Therapy Targeting Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen.J Nucl Med. 2015 Sep;56(9):1401-1407. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.155929. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 26182968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajasekaran AK, Anilkumar G, Christiansen JJ. Is prostate-specific membrane antigen a multifunctional protein? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;288:C975–81. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh A, Heston WD. Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2004;91:528–39. - PubMed
-
- Wright GL, Jr., Grob BM, Haley C, et al. Upregulation of prostate-specific membrane antigen after androgen-deprivation therapy. Urology. 1996;48:326–34. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland DW, Mao Y, Sullivan KF. Centromeres and kinetochores: from epigenetics to mitotic checkpoint signaling. Cell. 2003;112:407–21. - PubMed
-
- Georgi AB, Stukenberg PT, Kirschner MW. Timing of events in mitosis. Curr Biol. 2002;12:105–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

