Influence of antiretroviral drugs on the pharmacokinetics of prednisolone in HIV-infected individuals
- PMID: 18645517
- PMCID: PMC2669927
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31817bebeb
Influence of antiretroviral drugs on the pharmacokinetics of prednisolone in HIV-infected individuals
Abstract
Background: Corticosteroids are cytochrome P450 3A4 substrates, which have been associated with toxicities in patients receiving cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors such as human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors. In a study in healthy volunteers, ritonavir significantly increased prednisolone exposure.
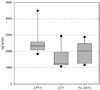
Methods: We investigated the influence of antiretroviral (ARV) medications on prednisolone pharmacokinetics in 3 groups of 10 human immunodeficiency virus-infected subjects. One group received lopinavir/ritonavir, and another efavirenz, as part of their ARV regimen; a third group did not receive ARV medications. Each subject received a single 20-mg prednisone dose followed by serial blood sampling for prednisolone. Prednisolone pharmacokinetics were compared among the groups.
Results: Area under the concentration-time curve was significantly lower in efavirenz recipients versus subjects receiving lopinavir/ritonavir (geometric mean ratio = 0.60, P = 0.01). Average prednisolone area under the concentration-time curve was higher in subjects taking lopinavir/ritonavir versus subjects not on ARVs; however, this difference was not significant (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: These data indicate that prednisolone concentrations may fluctuate widely when human immunodeficiency virus-positive individuals established on efavirenz therapy change to lopinavir/ritonavir or vice versa.
Figures
References
-
- Hogg RS, O-Shaughnessy MV, Gataric N, et al. Decline in deaths from AIDS due to new antiretrovirals. Lancet. 1997:349–1294. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Glesby MJ, Hoover DR, Vaamonde CM. Osteonecrosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: a case-control study. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Allison GT, Bostrom MP, Glesby MJ. Osteonecrosis in HIV disease: epidemiology, etiologies, and clinical management. AIDS. 2003;17:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Scribner AN, Troia-Cancio P, Cox BA, et al. Osteonecrosis in HIV: a case-control study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000;25:19–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

