Acupuncture for dysphagia in acute stroke
- PMID: 18646136
- PMCID: PMC12147868
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006076.pub2
Acupuncture for dysphagia in acute stroke
Abstract
Background: Dysphagia after acute stroke is associated with poor prognosis, particularly if prolonged. Acupuncture has been widely used for this complication in China. However, its therapeutic effect is unclear.
Objectives: To determine the therapeutic effect of acupuncture for dysphagia after acute stroke compared with placebo, sham or no acupuncture intervention.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register (last searched September 2007), the Chinese Stroke Trials Register and the Trials Register of the Cochrane Complementary Medicine Field (last searched January 2007) and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library, Issue 2, 2007). In January 2007 we searched the following databases from the first available date; MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, AMED, CISCOM, BIOSIS Previews, ProQuest Digital Dissertations, Science Citation Index, ISI Proceedings, ACUBRIEFS, ACP Journal Club, Books@Ovid and Journals@Ovid, Chinese Biological Medicine Database, Chinese scientific periodical database of VIP INFORMATION, China periodical in China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Evidence-Based Medicine Database, Science China, Chinese Social Science Citation Index, and the Chinese Science and Technology Document Databases. We also searched databases of ongoing trials, conference proceedings, and grey literature, handsearched three Chinese journals and contacted authors and researchers.
Selection criteria: We included all truly randomised controlled trials that evaluated the effect of acupuncture, irrespective of type, in patients with dysphagia within 30 day after the onset of ischaemic or haemorrhagic stroke. All types of acupuncture interventions were eligible. The control intervention could be placebo acupuncture, sham acupuncture, or no acupuncture. The primary outcome was recovery of normal feeding. The secondary outcomes were case fatality, deterioration, late disability, length of hospital stay, quality of life, feeding tube removal, aspiration pneumonia and nutritional measures.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected trials, assessed trial quality, and extracted data. Disagreements were resolved by a third review author.
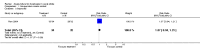
Main results: Only one trial of 66 participants was included. In the acupuncture group, 12 out of 34 participants recovered to normal feeding (35.3%). In the control group, seven out of 32 participants recovered to normal feeding (21.9%). The relative risk of recovery was 1.61 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.73 to 3.58. No statistical significance was detected.
Authors' conclusions: There is not enough evidence to make any conclusion about the therapeutic effect of acupuncture for dysphagia after acute stroke. High quality and large scale randomised controlled trials are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Han 2004 {published data only}
-
- Han JC. An observation on the therapeutic effect of acupuncture for bulbar palsy after acute stroke. Henan Journal of Practical Nervous Disease 2004;7(3):81‐2.
References to studies excluded from this review
Bai 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bai J, Li BD, Wang ZY, Gao WB, Wang LC. The role of different needling manipulation in adjusting swallow‐period obstacle of dysphagia after stroke. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 2007;27(1):35‐7. - PubMed
Bi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bi KP. Acupuncture for 160 patients with dysphagia following stroke. Chinese Folk Therapy 2004;12(2):17‐8.
Chen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chen Y, Li SY, Wang Y. The impression on deglutition disorders due to pseudo bulbar palsy treated with electroacupuncture integrated rehabilitation. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2003;7(3):430.
Chen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chen T. Observation on therapeutic effect of needling the Lianquan Point for dysphagia in acute cerebrovascular disease. Chinese pro‐seminar of dissertation compilation on cerebrovascular disease sponsored by the Chinese Medical Association. 2004.
Fu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fu YF, Zhan GX. Clinical observation on pseudo bulbar palsy after stroke treated by combinations of traditional Chinese herb, Western medicine and acupuncture. The 3rd Chinese Academic Conference of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine on Nervous System Diseases. Xi County, Anhui Province, 2000.
Fu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Fu TY, Duan YF. Acupuncture combined with rehabilitation exercise for dysphagia after stroke. Clinical Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2004;20(7):11‐2.
He 2002 {published data only}
-
- He XH, Zhou LB, Zhao XY. Rehabilitation of acupuncture for deglutition disorders due to cerebral infarction combining pseudo bulbar palsy. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2002;6(3):371‐2.
Hu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hu XL. Observation on acupuncture for sequelae of stroke. Journal of Corps Medicine 2005;1:13.
Lian 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lian QR. Clinical observation on early stroke treated by acupuncture. Clinical Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2003;19(2):15‐6.
Liao 2005 {published data only}
-
- Liao HW. Clinical observation on deglutition disorders following stroke treated by the combination of swallowing exercise and acupuncture. Guangxi Medical Journal 2005;27(1):18‐9.
Liu 1998 {published data only}
-
- Liu LL. Acupuncture treatment of bulbar palsy ‐ a report of 54 cases. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2000;20(1):30‐2. - PubMed
Liu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Liu KJ, Li JY, Cheng YL. Acupuncture and rehabilitation exercise for treating dysphagia in patients with pseudo bulbar palsy after stroke. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2003;18(9):536‐8.
Liu 2004a {published data only}
-
- Liu CR, Shi XQ, Zhang HQ. The application of acupuncture for deglutition disorders after pseudo palsy of stroke. Chinese Journal of Current Traditional and Western Medicine 2004;2(4):341‐2.
Liu 2004b {published data only}
-
- Liu GS. Observation on clinical effect in the treatment of 72 patients suffering from cerebrovascular infarction with the combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. New Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2004;36(10):55‐6.
Ma 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ma ZF. Clinical observation on the rehabilitation treatment of acute stroke treated by the combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Shenzhen Integrate Journal of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2003;13(5):307‐8.
Su 2004 {published data only}
-
- Su YB, Ma XQ, Gu LF. Integrated treatments for deglutition disorders after stroke. Chinese Rehabilitation 2004;19(5):305.
Wang 2003a {published data only}
-
- Wang HX, Li M, Dou ZH. Clinical observation on 30 cases of dysphagia in acute cerebrovascular disease treated by acupuncture. Chinese Clinical Research Journal of Medicine 2003;95:9540‐1.
Wang 2003b {published data only}
-
- Wang HM, Zhou GS, Liu Y, Tan J. Treatment of 30 cases of pseudo bulbar palsy with acupuncture combined with functional exercise. Chinese Journal of Physical Medicine Rehabilitation 2003;25(2):115‐6.
Wang 2003c {published data only}
-
- Wang YH, Leng FF. Clinical summary of acupuncture for 90 cases of pseudo bulbar palsy following acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medical 2003;23(6):437.
Wang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wang BQ, Han GS, Zhao JB, Wang WJ. Scalp acupuncture for deglutition disorders due to bulbar palsy of apoplexy. Jilin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2004;24(9):49.
Wei 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wei XD, Wan JX. Acupuncture for dysphagia in acute cerebrovascular disease. Practical Clinical Emergency by an Integration of Western Medicine and Chinese Medicine 1995;2(1):34‐5.
Xu 2001 {published data only}
-
- Xu J, He SY, Pang SH. Acupuncture for the dysphagic stroke due to pseudo bulbar palsy. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2001;17(8):14‐5.
Xue 2004 {published data only}
-
- Xue W, Gan LL. Early rehabilitation with acupuncture treatment on patients with allo‐swallowing because of pseudo‐medulla oblongata paralysis after apoplexy. Chinese Journal of Composite Clinical Medicine 2004;6(12):25‐6.
Yang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Yang QL, Huang ZW, Liu F, You QJ, Gao S, Hu JR, et al. Observation of clinical therapeutic effect of acupuncture and sublingual blood letting for treatment of pseudobulbar paralysis. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 2002;13(4):251‐4.
Zhang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zhang JR. Acupuncture for 30 cases of pseudo bulbar palsy due to stroke. Beijing Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2004;23(1):41‐2.
Zhao 1997b {published data only}
-
- Zhao GM, Xing HJ, Sun XC, Li XJ, Jiang JX. Clinical observation on 50 cases of dysphagia in acute cerebrovascular diseases treated by dialectical acupuncture. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 1997;17(2):97.
Zhong 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zhong JB, Jin DN. Clinical observation on hyperbaric oxygen combined with electroacupuncture for dysphagia following cerebrovascular infarction. Family Medical Journal 2005;21(3):290‐1.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Seki 2005 {published data only}
-
- Seki T, Iwasaki K, Arai H, Sasaki H, Hayashi H, Yamada S, et al. Acupuncture for dysphagia in poststroke patients: a videofluoroscopic study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2005;53(6):1083‐4. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Heng 1999 {published data only}
-
- Heng D. Acupuncture adjuvant therapy for dysphagia due to recent stroke. NMRC's Clinical Trials and Epidemiology Research Unit, Singapore. Annual Report 1999. http://www.cteru.gov.sg 1999. [CN‐00324852]
Heng 2001 {published data only}
-
- Heng D, Lim SH, Cui SL, Zhou Q, Chang HM, Chen C, et al. SQACU01‐ a randomised trial of acupuncture as adjuvant therapy for dysphagia due to recent stroke. Clinical Trials and Epidemiology Research Unit, Singapore 2001. [CN‐00387867]
Additional references
Chen 2003b
-
- Chen RY, Lim JK, Chuo AM. Stroke audit. Medical Journal of Malaysia 2003;58(3):330‐6. - PubMed
Crary 2004
-
- Crary MA, Carnaby Mann GD, Groher ME, Helseth E. Functional benefits of dysphagia therapy using adjunctive sEMG biofeedback. Dysphagia 2004;19(3):160‐4. - PubMed
Daniels 1999
-
- Daniels SK, Brailey K, Foundas AL. Lingual discoordination and dysphagia following acute stroke: analyses of lesion localization. Dyaphagia 1999;14(2):85‐92. - PubMed
Deeks 2001
-
- Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta‐analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta‐analysis in Context. 2nd Edition. London: BMJ Publication Group, 2001.
Duncan 2000
-
- Duncan PW, Jorgensen HS, Wade DT. Outcome measures in acute stroke trials: a systematic review and some recommendations to improve practice. Stroke 2000;31:1429‐38. - PubMed
Dziewas 2004
Egger 1997
EHTAG 1999
FOOD 2005
-
- The FOOD Trial Collaboration. Effect of timing and method of enteral tube feeding for dysphagic stroke patients (FOOD): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005;365:764‐72. - PubMed
Furlan 2005
Gordon 1987
Han 2007
-
- Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW, Kwon BS. The prediction of persistent dysphagia beyond six months after stroke. Dysphagia 2008;23(1):59‐64. - PubMed
Hatano 1976
Iizuka 2005
-
- Iizuka M, Reding M. Use of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy feeding tubes and functional recovery in stroke rehabilitation: a case‐matched controlled study. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2005;86(5):1049‐52. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jada AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Jiang 1992
-
- Jiang GL, Shi XM, Zhang CS, Hu GQ, Liu YJ. The clinical and experimental study on acupuncture therapy of 'Arousing the brain and opening the orifice' for pseudo bulbar palsy. Tianjin Medication 1992;3:168‐71.
Kappelle 2004
-
- Kappelle LJ, Worp HB. Treatment or prevention of complications of acute ischemic stroke. Current Neurology & Neuroscience Reports 2004;4(1):36‐41. - PubMed
Lazarra 1986
-
- Lazarra G, Lazarus C, Logemann J. Impact of thermal stimulation on the triggering of the swallow reflex. Dysphagia 1986;1:73‐7.
Liu 2000
-
- Liu LL. Acupuncture treatment of bulbar palsy ‐ a report of 54 cases. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2000;20(1):30‐2. - PubMed
Logemann 1991
-
- Logemann JA. Approaches to management of disordered swallowing. Baillieres Clinical Gastroenterology 1991;5(2):269‐80. - PubMed
MacPherson 2002
-
- MacPherson H, White A, Cummings M, Jobst KA, Rose K, Niemtzow RC for the STRICTA Group. Standards for reporting interventions in controlled trials of acupuncture: the STRICTA recommendations. Journal of Alternative Complementary Medicine 2002;8(1):85‐9. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG, for the CONSORT Group. The CONSORT Statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;134:657‐62. - PubMed
Murray 1997
-
- Murray CJL, Lopez AD. Mortality by cause for eight regions of the world: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997;349(3):1269‐76. - PubMed
Norton 1996
Nowicki 2003
-
- Nowicki NC, Averill A. Acupuncture for dysphagia following stroke. Medical Acupuncture 2003;14(3):17‐9.
O'Neill 2000
-
- O'Neill PA. Swallowing and prevention of complications. British Medical Bulletin 2000;56(2):457‐65. - PubMed
Odderson 1995
-
- Odderson IR, Keaton JC, McKenna BS. Swallow management in patients on an acute stroke pathway: quality is cost effective. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 1995;76(12):1130‐3. - PubMed
Paciaroni 2004
-
- Paciaroni M, Mazzotta G, Corea F, Caso V, Venti M, Milia P, et al. Dysphagia following stroke. European Neurology 2004;51(3):162‐7. - PubMed
PEGASUS 1998
-
- Davies S, Fall S, Ellul Y, Barer D, on behalf of the PEGASUS Trial Collaborators. Dysphagia and nutrition after stroke: should more patients be considered for early percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) feeding?. Clinical Rehabilitation 1998;12:162.
Runions 2004
-
- Runions S, Rodrigue N, White C. Practice on an acute stroke unit after implementation of a decision‐making algorithm for dietary management of dysphagia. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing 2004;36(4):200‐7. - PubMed
Sami 2005
-
- Sami A, Kenneth D. Dysphagia in aging. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2005;39(5):357‐71. - PubMed
SCSSS 1999
-
- Swedish Collaboration on Sensory Stimulation in Stroke. Sensory stimulation after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Disorders 1999;9 Suppl 1:28.
Seki 2003
-
- Seki T, Kurusu M, Tanji H, Ariai H, Sasaki H. Acupuncture and swallowing reflex in poststroke patients. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(5):726‐7. - PubMed
Shi 1999
-
- Shi XM, Yang ZG, Zhou JZ, Han JX, Zhang CS, Bian JL, et al. Clinical and mechanical study on acupuncture for 325 cases of pseudo bulbar palsy. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 1999;19(8):491‐4.
Smithard 1996
-
- Smithard DG, O'Neill PA, Park C, Morris J, Wyatt R, England R, et al. Complications and outcome after acute stroke. Does dysphagia matter?. Stroke 1996;27:1200‐4. - PubMed
Smithard 1998a
-
- Smithard DG, O'Neill PA, Park C. Can bedside assessment reliably exclude aspiration following acute stroke?. Age & Ageing 1998;27:99‐106. - PubMed
Smithard 1998b
-
- Smithard DG, O'Neill PA, England RE, Park CL, Wyatt R, Martin DF, et al. The natural history of dysphagia following a stroke. Dysphagia 1998;13(1):32‐8. - PubMed
STAIR II 2001
-
- Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable II (STAIR‐II). Recommendations for clinical trial evaluation of acute stroke therapies. Stroke 2001;32:1598‐606. - PubMed
Teasell 2005
-
- Teasell R, Foley N. Results from the FOOD trial. Lancet Neurology 2005;4(5):267. - PubMed
Wang 2001
-
- Wang JL. Clinical Epidemiology. 2nd Edition. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, 2001:138.
Yang 2002
-
- Yang QL, Huang ZW, Liu F, You QJ, Gao S, Hu JR, et al. Treatment of pseudobulbar paralysis with acupuncture and sublingual blood‐letting. International Journal of Clinical Acupuncture 2002;13(4):251‐4.
Zhao 1997a
-
- Zhao XM. Acupuncture for 30 cases of progressive bulbar palsy. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 1997;16(1):14.
Zhao 2001
-
- Zhao CQ, Zhang YF. Use of the therapeutic principle of 'Opening the orifice and suppressing the upsurge' for treating 13 dysphagic cases by acupuncture. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 2001;21(10):586.
Zhong 2003
-
- Zhong CM, Rong G, He FZ, Jin HY. Comparison of head and body acupuncture in the treatment of deglutition disorders in the subacute period of stroke. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2003;7(19):2076‐7.
Zou 2004
-
- Zou HJ, Zhao WM. Therapeutic effect of acupuncture on dysphagia due to pseudobulbar palsy. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 2004;24(4):7‐8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical