Disruption of the p53-Mdm2 complex by Nutlin-3 reveals different cancer cell phenotypes
- PMID: 18646312
- PMCID: PMC3535287
Disruption of the p53-Mdm2 complex by Nutlin-3 reveals different cancer cell phenotypes
Abstract
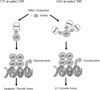
Introduction: Mdm2 inhibits p53 transactivation by forming a p53-Mdm2 complex on chromatin. Upon DNA damage-induced complex disruption, such latent p53 can be activated, but in cells overexpressing Mdm2 because of a homozygous single nucleotide polymorphism at position 309 (T --> G) of mdm2, the complex is highly stable and cannot be disrupted by DNA damage, rendering p53 inactive.
Methods: To determine whether the p53 response phenotype is influenced differentially in cells with variable mdm2 genotypes, we compared responses to DNA damage and targeted p53-Mdm2 complex disruption by Nutlin-3 in the following wild-type p53 human cancer cell lines: A875 and CCF-STTG-1 (G/G for mdm2 SNP309), SJSA-1 (mdm2 genomic amplification and T/T for mdm2 SNP309), MCF-7 (estrogen-induced Mdm2 overexpression and T/G for mdm2 SNP309), ML-1 and H460 (T/T for mdm2 SNP309), and K562 (p53-null and T/G for mdm2 SNP309). We also examined mdm2 gene-splicing patterns in these lines by cloning and sequencing analyses.
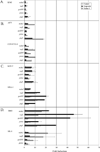
Results: While Mdm2-overexpressing G/G cells were resistant to p53 activation by DNA damage, they were sensitive to Nutlin-3. Strikingly, the p53 G1 checkpoint in G/G cells was activated by Nutlin-3 but not by etoposide, whereas in other Mdm2-overexpressing cells, both drugs activated p53 and subsequent G1 arrest or apoptosis. cDNA clones lacking exons 5-9 were generated at a high frequency in cells overexpressing Mdm2.
Conclusion: Nutlin-3 and DNA damage distinguish a differential phenotype in human cancer cells with G/G mdm2 SNP309 from other Mdm2 overexpressers. Categorization of the Mdm2 isoforms produced and their influence on p53 activity will help in characterization and treatment development for different cancers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of the p53 pathway by the MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3a overcomes BCL2 overexpression in a preclinical model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with t(14;18)(q32;q21).Leukemia. 2011 May;25(5):856-67. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.28. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21394100 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin in Combination with MDM2 Inhibition Downregulates Rad51 Recombinase in a Bimodal Manner to Inhibit Homologous Recombination and Augment Tumor Cell Kill.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;97(4):237-249. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.117564. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32063580 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygous mdm2 SNP309 cancer cells with compromised transcriptional elongation at p53 target genes are sensitive to induction of p53-independent cell death.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34573-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5312. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26416444 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic activation of p53 by small-molecule MDM2 antagonists.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(6):560-8. doi: 10.2174/138161211795222603. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21391906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the therapeutic perspectives of Nutlin-3.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(6):569-77. doi: 10.2174/138161211795222586. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21391907 Review.
Cited by
-
Idasanutlin plus cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: results of the MIRROS trial.Blood Adv. 2022 Jul 26;6(14):4147-4156. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006303. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35413116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transcription-associated DNA DSBs activate p53 during hiPSC-based neurogenesis.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 15;12(1):12156. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16516-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35840793 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing up mdm2 for cancer proteome diversity.Genes Cancer. 2012 Mar;3(3-4):311-9. doi: 10.1177/1947601912455323. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23150764 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2/MDMX inhibition by Sulanemadlin synergizes with anti-Programmed Death 1 immunotherapy in wild-type p53 tumors.iScience. 2024 May 6;27(6):109862. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109862. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38784022 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic screening identifies PML/p53 axis as a potential treatment target of facial nerve schwannomas.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):4237-4250. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32913501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reihsaus E, Kohler M, Kraiss S, Oren M, Montenarh M. Regulation of the level of the oncoprotein p53 in non-transformed and transformed cells. Oncogene. 1989;5:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Bargonetti J, Manfredi JJ. Multiple roles of the tumor suppressor p53. Curr Opin Oncol. 2002;14:86–91. - PubMed
-
- Toledo F, Wahl GM. Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:909–923. - PubMed
-
- White DE, Talbott KE, Arva NC, Bargonetti J. Mouse double minute 2 associates with chromatin in the presence of p53 and is released to facilitate activation of transcription. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3463–3470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
