Generation of multilayered structures for biomedical applications using a novel tri-needle coaxial device and electrohydrodynamic flow
- PMID: 18647737
- PMCID: PMC3226996
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0247
Generation of multilayered structures for biomedical applications using a novel tri-needle coaxial device and electrohydrodynamic flow
Abstract
In this short communication, we describe the scope and flexibility of using a novel device containing three coaxially arranged needles to form a variety of novel morphologies. Different combinations of materials are subjected to controlled flow through the device under the influence of an applied electric field. The resulting electrohydrodynamic flow allows us to prepare double-layered bubbles, porous encapsulated threads and nanocapsules containing three layers. The ability to process such multilayered structures is very significant for biomedical engineering applications, for example, generating capsules for drug delivery, which can provide multistage controlled release.
Figures
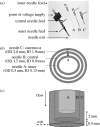
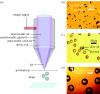
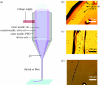
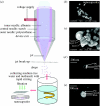
References
-
- Barrero A, Loscertales I.G. Micro- and nanoparticles via capillary flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2007;39:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.39.050905.110245. - DOI
-
- Borra J.P, Tombette Y, Ehouarn P. Influence of electric field profile and polarity on the mode of EHDA related to electric discharge regimes. J. Aerosol Sci. 1999;30:913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0021-8502(98)00779-4. - DOI
-
- Chen C.H, Emond M.H.J, Kelder E.M, Meester B, Schoonman J. Electrostatic sol-spray deposition of nanostructured ceramic thin films. J. Aerosol Sci. 1999;30:959–967. doi: 10.1016/S0021-8502(98)00075-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

