Temporal neuropathologic and behavioral phenotype of 6neo/6neo Pompe disease mice
- PMID: 18648322
- PMCID: PMC2743262
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181815994
Temporal neuropathologic and behavioral phenotype of 6neo/6neo Pompe disease mice
Abstract
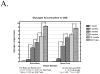
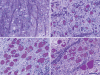
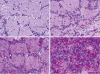
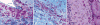
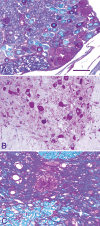
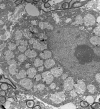
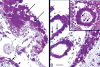
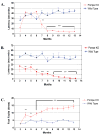
Pompe disease (glycogen storage disease II) is caused by mutations in the acid alpha-glucosidase gene. The most common form is rapidly progressive with glycogen storage, particularly in muscle, which leads to profound weakness, cardiac failure, and death by the age of 2 years. Although usually considered a muscle disease, glycogen storage also occurs in the CNS. We evaluated the progression of neuropathologic and behavioral abnormalities in a Pompe disease mouse model (6neo/6neo) that displays many features of the human disease. Homozygous mutant mice store excess glycogen within large neurons of hindbrain, spinal cord, and sensory ganglia by the age of 1 month; accumulations then spread progressively within many CNS cell types. "Silver degeneration" and Fluoro-Jade C stains revealed severe degeneration in axon terminals of primary sensory neurons at 3 to 9 months. These abnormalities were accompanied by progressive behavioral impairment on rotorod, wire hanging, and foot fault tests. The extensive neuropathologic alterations in this model suggest that therapy of skeletal and cardiac muscle disorders by systemic enzyme replacement therapy may not be sufficient to reverse functional deficits due to CNS glycogen storage, particularly early-onset, rapidly progressive disease. A better understanding of the basis for clinical manifestations is needed to correlate CNS pathology with Pompe disease manifestations.
Figures





References
-
- Pompe JC. Over idiopathische hypertrophie van het hart. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1932;76:304–11.
-
- Hirshhorn R, Reuser A. Glycogen Storage Disease Type II: Acid alpha-glucosidase (acid maltase) deficiency. In: Schriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 3389–420.
-
- Cori GT. Glycogen structure and enzyme deficiencies in glycogen storage disease. Harvey Lect. 1954;8:145–71. - PubMed
-
- Reuser AJ, Drost MR. Lysosomal dysfunction, cellular pathology and clinical symptoms: Basic principles. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2006;95:77–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

