Cheating on the edge
- PMID: 18648645
- PMCID: PMC2453231
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002763
Cheating on the edge
Abstract
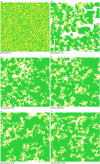
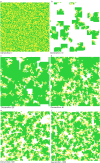
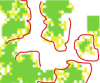
We present the results of an individual agent-based model of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Our model examines antibiotic resistance when two strategies exist: "producers"--who secrete a substance that breaks down antibiotics--and nonproducers ("cheats") who do not secrete, or carry the machinery associated with secretion. The model allows for populations of up to 10,000, in which bacteria are affected by their nearest neighbors, and we assume cheaters die when there are no producers in their neighborhood. Each of 10,000 slots on our grid (a torus) could be occupied by a producer or a nonproducer, or could (temporarily) be unoccupied. The most surprising and dramatic result we uncovered is that when producers and nonproducers coexist at equilibrium, nonproducers are almost always found on the edges of clusters of producers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Williams G. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1966. Adaptation and Natural Selection.
-
- Dawkins R. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1976. The Selfish Gene.
-
- Wilson DS. Menlo Park: Benjamin Cummings; 1980. The Natural Selection of Populations and Communities.
-
- Sober E, Wilson DS. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1998. Unto Others.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

