Regional susceptibility to domoic acid in primary astrocyte cells cultured from the brain stem and hippocampus
- PMID: 18648670
- PMCID: PMC2474954
Regional susceptibility to domoic acid in primary astrocyte cells cultured from the brain stem and hippocampus
Abstract
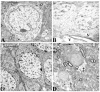
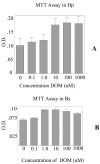
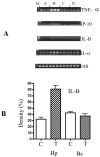
Domoic acid is a marine biotoxin associated with harmful algal blooms and is the causative agent of amnesic shellfish poisoning in marine animals and humans. It is also an excitatory amino acid analog to glutamate and kainic acid which acts through glutamate receptors eliciting a very rapid and potent neurotoxic response. The hippocampus, among other brain regions, has been identified as a specific target site having high sensitivity to DOM toxicity. Histopathology evidence indicates that in addition to neurons, the astrocytes were also injured. Electron microscopy data reported in this study further supports the light microscopy findings. Furthermore, the effect of DOM was confirmed by culturing primary astrocytes from the hippocampus and the brain stem and subsequently exposing them to domoic acid. The RNA was extracted and used for biomarker analysis. The biomarker analysis was done for the early response genes including c-fos, c-jun, c-myc, Hsp-72; specific marker for the astrocytes- GFAP and the glutamate receptors including GluR 2, NMDAR 1, NMDAR 2A and B. Although, the astrocyte-GFAP and c-fos were not affected, c-jun and GluR 2 were down-regulated. The microarray analysis revealed that the chemokines / cytokines, tyrosine kinases (Trk), and apoptotic genes were altered. The chemokines that were up-regulated included - IL1-alpha, IL-Beta, IL-6, the small inducible cytokine, interferon protein 10P-10, CXC chemokine LIX, and IGF binding proteins. The Bax, Bcl-2, Trk A and Trk B were all down-regulated. Interestingly, only the hippocampal astrocytes were affected. Our findings suggest that astrocytes may present a possible target for pharmacological interventions for the prevention and treatment of amnesic shellfish poisoning and for other brain pathologies involving excitotoxicity.
Keywords: Domoic acid; astrocytes; electron microscopy; semi-quantitative analysis; susceptibility.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective role of melatonin in domoic acid-induced neuronal damage in the hippocampus of adult rats.Hippocampus. 2003;13(3):375-87. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10090. Hippocampus. 2003. PMID: 12722978
-
Effect of a short-term in vitro exposure to the marine toxin domoic acid on viability, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and superoxide anion release by rat neonatal microglia.BMC Pharmacol. 2001;1:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-1-7. Epub 2001 Oct 2. BMC Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11686853 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic actions of the amnesic shellfish poison, domoic acid.Neuroreport. 1994 Apr 14;5(8):981-5. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199404000-00032. Neuroreport. 1994. PMID: 8061308
-
Risk assessment of the amnesic shellfish poison, domoic acid, on animals and humans.J Environ Biol. 2009 May;30(3):319-25. J Environ Biol. 2009. PMID: 20120452 Review.
-
Domoic acid and human exposure risks: a review.Toxicon. 2010 Aug 15;56(2):218-30. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.05.034. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 19505488 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of metallothioneins in cell therapy and nanomedicine.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1477-88. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S42019. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23620664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for association between hepatitis C virus and Parkinson's disease.Neurol Sci. 2017 Nov;38(11):1913-1920. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3077-4. Epub 2017 Aug 5. Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28780707 Review.
-
Domoic acid toxicologic pathology: a review.Mar Drugs. 2008 May 28;6(2):180-219. doi: 10.3390/md20080010. Mar Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18728725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated low level domoic acid exposure increases CA1 VGluT1 levels, but not bouton density, VGluT2 or VGAT levels in the hippocampus of adult mice.Harmful Algae. 2018 Nov;79:74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Harmful Algae. 2018. PMID: 30420019 Free PMC article.
-
The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jan 29;23(2):61. doi: 10.3390/md23020061. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aschner M. Astrocytic functions and physiological reactions to injury: the potential to induce and/or exacerbate neuronal dysfunction--a forum position paper. Neurotoxicology. 1998;19:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Aschner M. Immune and inflammatory responses in the CNS: modulation by astrocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 1998;102-103:283–287. - PubMed
-
- Aschner M. Neuron-astrocyte interactions: implications for cellular energetics and antioxidant levels. Neurotoxicology. 2001;21:1101–1107. - PubMed
-
- Verkhratsky A. Glial calcium: homeostasis and signalling function. Physiol. Rev. 1998;78:99–141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
