Estimating cerebral oxygen metabolism from fMRI with a dynamic multicompartment Windkessel model
- PMID: 18649348
- PMCID: PMC2670946
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20628
Estimating cerebral oxygen metabolism from fMRI with a dynamic multicompartment Windkessel model
Abstract
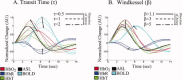
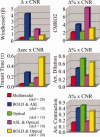
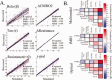
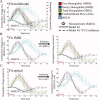
Stimulus evoked changes in cerebral blood flow, volume, and oxygenation arise from responses to underlying neuronally mediated changes in vascular tone and cerebral oxygen metabolism. There is increasing evidence that the magnitude and temporal characteristics of these evoked hemodynamic changes are additionally influenced by the local properties of the vasculature including the levels of baseline cerebral blood flow, volume, and blood oxygenation. In this work, we utilize a physiologically motivated vascular model to describe the temporal characteristics of evoked hemodynamic responses and their expected relationships to the structural and biomechanical properties of the underlying vasculature. We use this model in a temporal curve-fitting analysis of the high-temporal resolution functional MRI data to estimate the underlying cerebral vascular and metabolic responses in the brain. We present evidence for the feasibility of our model-based analysis to estimate transient changes in the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO(2)) in the human motor cortex from combined pulsed arterial spin labeling (ASL) and blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) MRI. We examine both the numerical characteristics of this model and present experimental evidence to support this model by examining concurrently measured ASL, BOLD, and near-infrared spectroscopy to validate the calculated changes in underlying CMRO(2).
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



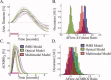
References
-
- Bamber D,van Santen JP ( 2000): How to assess a model's testability and identifiability. J Math Psychol 44: 20–40. - PubMed
-
- Belliveau JW,Kennedy DN Jr,McKinstry RC,Buchbinder BR,Weisskoff RM,Cohen MS,Vevea JM,Brady TJ,Rosen BR ( 1991): Functional mapping of the human visual cortex by magnetic resonance imaging. Science 254: 716–719. - PubMed
-
- Boas DA,Strangman G,Culver JP,Hoge RD,Jasdzewski G,Poldrack RA,Rosen BR,Mandeville JB ( 2003): Can the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen be estimated with near‐infrared spectroscopy? Phys Med Biol 48: 2405–2418. - PubMed
-
- Boxerman JL,Bandettini PA,Kwong KK,Baker JR,Davis TL,Rosen BR,Weisskoff RM ( 1995): The intravascular contribution to fMRI signal change: Monte Carlo modeling and diffusion‐weighted studies in vivo. Magn Reson Med 34: 4–10. - PubMed
-
- Buxton RB,Uludag K,Dubowitz DJ,Liu TT ( 2004): Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation. Neuroimage 23( Suppl. 1): S220–S233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

