HASTE sequence with parallel acquisition and T2 decay compensation: application to carotid artery imaging
- PMID: 18650045
- PMCID: PMC2630054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2008.05.009
HASTE sequence with parallel acquisition and T2 decay compensation: application to carotid artery imaging
Abstract
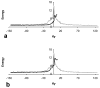
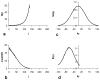
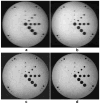
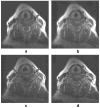
T2-weighted carotid artery images acquired using the turbo spin-echo (TSE) sequence frequently suffer from motion artifacts due to respiration and blood pulsation. The possibility of using HASTE sequence to achieve motion-free carotid images was investigated. The HASTE sequence suffers from severe blurring artifacts due to signal loss in later echoes due to T2 decay. Combining HASTE with parallel acquisition (PHASTE) decreases the number of echoes acquired and thus effectively reduces the blurring artifact caused by T2 relaxation. Further improvement in image sharpness can be achieved by performing T2 decay compensation before reconstructing the PHASTE data. Preliminary results have shown successful suppression of motion artifacts with PHASTE imaging. The image quality was enhanced relative to the original HASTE image, but was still less sharp than a non-motion-corrupted TSE image.
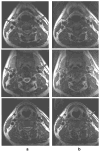
Figures


References
-
- Nozaki A. Single shot fast spin echo (SSFSE) Nippon Rinsho. 1998;56(11):2792–7. - PubMed
-
- Noll DC, Nishimura DG, Macovski A. Homodyne detection in magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1991;10(2):154–63. - PubMed
-
- Terk MR, et al. Halfscan: clinical applications in MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1991;9(4):477–83. - PubMed
-
- Mirowitz SA, et al. Rapid acquisition spin-echo (RASE) MR imaging: a new technique for reduction of artifacts and acquisition time. Radiology. 1990;175(1):131–5. - PubMed
-
- Semelka RC, et al. HASTE MR imaging: description of technique and preliminary results in the abdomen. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1996;6(4):698–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

