Characteristics and prediction of RNA editing sites in transcripts of the Moss Takakia lepidozioides chloroplast
- PMID: 18650260
- PMCID: PMC2575889
- DOI: 10.1093/dnares/dsn016
Characteristics and prediction of RNA editing sites in transcripts of the Moss Takakia lepidozioides chloroplast
Abstract
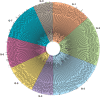
RNA editing in land plant organelles is a process primarily involving the conversion of cytidine to uridine in pre-mRNAs. The process is required for gene expression in plant organelles, because this conversion alters the encoded amino acid residues and improves the sequence identity to homologous proteins. A recent study uncovered that proteins encoded in the nuclear genome are essential for editing site recognition in chloroplasts; the mechanisms by which this recognition occurs remain unclear. To understand these mechanisms, we determined the genomic and cDNA sequences of moss Takakia lepidozioides chloroplast genes, then computationally analyzed the sequences within -30 to +10 nucleotides of RNA editing sites (neighbor sequences) likely to be recognized by trans-factors. As the T. lepidozioides chloroplast has many RNA editing sites, the analysis of these sequences provides a unique opportunity to perform statistical analyses of chloroplast RNA editing sites. We divided the 302 obtained neighbor sequences into eight groups based on sequence similarity to identify group-specific patterns. The patterns were then applied to predict novel RNA editing sites in T. lepidozioides transcripts; approximately 60% of these predicted sites are true editing sites. The success of this prediction algorithm suggests that the obtained patterns are indicative of key sites recognized by trans-factors around editing sites of T. lepidozioides chloroplast genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The complete plastid genome sequence of the enigmatic moss, Takakia lepidozioides (Takakiopsida, Bryophyta): evolutionary perspectives on the largest collection of genes in mosses and the intensive RNA editing.Plant Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;107(4-5):431-449. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01214-z. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Plant Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34817767
-
Extensive RNA editing in transcripts from the PsbB operon and RpoA gene of plastids from the enigmatic moss Takakia lepidozioides.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2006 Sep;70(9):2268-74. doi: 10.1271/bbb.60204. Epub 2006 Sep 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16960353
-
RNA editing in the anticodon of tRNA Leu (CAA) occurs before group I intron splicing in plastids of a moss Takakia lepidozioides S. Hatt. & Inoue.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008 Mar;10(2):250-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2007.00027.x. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008. PMID: 18304199
-
Sense from nonsense: how the genetic information of chloroplasts is altered by RNA editing.Biochimie. 2000 Jun-Jul;82(6-7):549-57. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(00)00610-6. Biochimie. 2000. PMID: 10946106 Review.
-
Evolution and mechanism of translation in chloroplasts.Annu Rev Genet. 1998;32:437-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.32.1.437. Annu Rev Genet. 1998. PMID: 9928487 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Evolutionary Study of Chloroplast RNA Editing in Gymnosperms: A Novel Type of G-to-A RNA Editing Is Common in Gymnosperms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10844. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810844. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142757 Free PMC article.
-
Variable frequency of plastid RNA editing among ferns and repeated loss of uridine-to-cytidine editing from vascular plants.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 8;10(1):e0117075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117075. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25568947 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional control of chloroplast gene expression.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2009 Mar 12;3:31-47. doi: 10.4137/grsb.s2080. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2009. PMID: 19838333 Free PMC article.
-
RESOPS: a database for analyzing the correspondence of RNA editing sites to protein three-dimensional structures.Plant Cell Physiol. 2009 Nov;50(11):1865-73. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcp132. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19808808 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear DYW-type PPR gene families diversify with increasing RNA editing frequencies in liverwort and moss mitochondria.J Mol Evol. 2012 Feb;74(1-2):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s00239-012-9486-3. J Mol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22302222
References
-
- Bock R. Sense from nonsense: how the genetic information of chloroplasts is altered by RNA editing. Biochimie. 2000;82:549–557. - PubMed
-
- Covello P. S., Gray M. W. RNA editing in plant mitochondria. Nature. 1989;341:662–666. - PubMed
-
- Hoch B., Maier R. M., Appel K., Igloi G. L., Kössel H. Editing of a chloroplast mRNA by creation of an initiation codon. Nature. 1991;353:178–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

