Generation of enhanced stability factor VIII variants by replacement of charged residues at the A2 domain interface
- PMID: 18650448
- PMCID: PMC2556611
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-142158
Generation of enhanced stability factor VIII variants by replacement of charged residues at the A2 domain interface
Abstract
Factor VIII consists of a heavy chain (A1A2B domains) and light chain (A3C1C2 domains), whereas the contiguous A1A2 domains are separate subunits in the cofactor, factor VIIIa. The intrinsic instability of the cofactor results from weak affinity interactions of the A2 subunit within factor VIIIa. The charged residues Glu272, Asp519, Glu665, and Glu1984 appear buried at the interface of the A2 domain with either the A1 or A3 domain, and thus may impact protein stability. To determine the effects of these residues on procofactor/cofactor stability, these residues were individually replaced with either Ala or Val, and stable BHK cell lines expressing the B-domainless proteins were prepared. Specific activity and thrombin generation parameters for 7 of the 8 variants were more than 80% the wild-type value. Factor VIII activity at 52 degrees C to 60 degrees C and the decay of factor VIIIa activity after thrombin activation were monitored. Six of the 7 variants showing wild-type-like activity demonstrated enhanced stability, with the Glu1984Val variant showing a 2-fold increase in thermostability and an approximately 4- to 8-fold increase in stability of factor VIIIa. These results indicate that replacement of buried charged residues is an effective alternative to covalent modification in increasing factor VIII (VIIIa) stability.
Figures
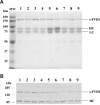
 ) and 2-stage chromogenic factor Xa generation assay (■). (B,C) Thrombogram of factor VIII proteins. WT (
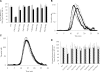
) and 2-stage chromogenic factor Xa generation assay (■). (B,C) Thrombogram of factor VIII proteins. WT ( ), Glu272Ala (□), Glu272Val (■), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), and Glu1984Val (♦). (D) Parameter values obtained from thrombin generation assays. Thrombograms show the average values of triplicated samples. The parameter values were expressed as values (%) relative to WT. The actual values for WT were 7.5 plus or minus 0.5 minutes (lag time), 13.7 plus or minus 0.3 minutes (peak time), 157.3 plus or minus 14.7 nM (peak value), and 979.8 plus or minus 37.9 nM/min (ETP). Lag time (□), peak time (
), Glu272Ala (□), Glu272Val (■), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), and Glu1984Val (♦). (D) Parameter values obtained from thrombin generation assays. Thrombograms show the average values of triplicated samples. The parameter values were expressed as values (%) relative to WT. The actual values for WT were 7.5 plus or minus 0.5 minutes (lag time), 13.7 plus or minus 0.3 minutes (peak time), 157.3 plus or minus 14.7 nM (peak value), and 979.8 plus or minus 37.9 nM/min (ETP). Lag time (□), peak time ( ), peak value (■), and ETP (▧). Error bars represent SD values averaged from 3 separate determinations.
), peak value (■), and ETP (▧). Error bars represent SD values averaged from 3 separate determinations.
 , ×), Glu272Ala (□), Glu272Val (■), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), Glu1984Val (♦), and full-length Kogenate factor VIII (
, ×), Glu272Ala (□), Glu272Val (■), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), Glu1984Val (♦), and full-length Kogenate factor VIII ( ). (A) Representative factor VIII decay curves after 55°C incubation. (B) Plots of factor VIII decay rate at various temperatures. (Inset) Magnified view of the decay results incubated at 52°C to 55°C.
). (A) Representative factor VIII decay curves after 55°C incubation. (B) Plots of factor VIII decay rate at various temperatures. (Inset) Magnified view of the decay results incubated at 52°C to 55°C.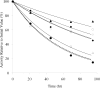
 , ×), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), and Glu1984Val (♦). Data were fitted by nonlinear least squares regression, and each point represents the value averaged from 3 separate determinations.
, ×), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), and Glu1984Val (♦). Data were fitted by nonlinear least squares regression, and each point represents the value averaged from 3 separate determinations.
 , ×), Glu272Ala (□), Glu272Val (■), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), and Glu1984Val (♦). Data were fitted by nonlinear least squares regression, and each point represents the value averaged from 3 separate determinations.
, ×), Glu272Ala (□), Glu272Val (■), Asp519Ala (○), Asp519Val (●), Glu665Ala (△), Glu665Val (▲), Glu1984Ala (◇), and Glu1984Val (♦). Data were fitted by nonlinear least squares regression, and each point represents the value averaged from 3 separate determinations.
References
-
- Fay PJ. Activation of factor VIII and mechanisms of cofactor action. Blood Rev. 2004;18:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Fay PJ. Reconstitution of human factor VIII from isolated subunits. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988;262:525–531. - PubMed
-
- Ansong C, Miles SM, Fay PJ. Factor VIII A1 domain residues 97-105 represent a light chain-interactive site. Biochemistry. 2006;45:13140–13149. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman RJ, Pipe SW. Regulation of factor VIII expression and activity by von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi H, Koszelak ME, Mastri M, Fay PJ. Metal ion-independent association of factor VIII subunits and the roles of calcium and copper ions for cofactor activity and inter-subunit affinity. Biochemistry. 2001;40:10293–10300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

