Structure of the Roc-COR domain tandem of C. tepidum, a prokaryotic homologue of the human LRRK2 Parkinson kinase
- PMID: 18650931
- PMCID: PMC2519104
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.150
Structure of the Roc-COR domain tandem of C. tepidum, a prokaryotic homologue of the human LRRK2 Parkinson kinase
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2008 Sep 3;27(17):2352
Abstract
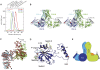
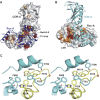
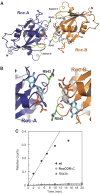
Ras of complex proteins (Roc) belongs to the superfamily of Ras-related small G-proteins that always occurs in tandem with the C-terminal of Roc (COR) domain. This Roc-COR tandem is found in the bacterial and eukaryotic world. Its most prominent member is the leucine-rich repeat kinase LRRK2, which is mutated and activated in Parkinson patients. Here, we investigated biochemically and structurally the Roco protein from Chlorobium tepidum. We show that Roc is highly homologous to Ras, whereas the COR domain is a dimerisation device. The juxtaposition of the G-domains and mutational analysis suggest that the Roc GTPase reaction is stimulated and/or regulated by dimerisation in a nucleotide-dependent manner. The region most conserved between bacteria and man is the interface between Roc and COR, where single-point Parkinson mutations of the Roc and COR domains are in close proximity. The analogous mutations in C. tepidum Roc-COR decrease the GTPase reaction rate, most likely due to a modification of the interaction between the Roc and COR domains.
Figures




References
-
- Barbacid M (1987) ras Genes. Ann Rev Biochem 56: 779–827 - PubMed
-
- Bosgraaf L, Van Haastert PJM (2003) Roc, a Ras/GTPase domain in complex proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta—Mol Cell Res 1643: 5–10 - PubMed
-
- Chavas LMG, Torii S, Kamikubo H, Kawasaki M, Ihara K, Kato R, Kataoka M, Izumi T, Wakatsuki S (2007) Structure of the small GTPase Rab27b shows an unexpected swapped dimer. Acta Crystallogr Sec D BiolCrystallogr 63: 769–779 - PubMed
-
- Eberth A, Dvorsky R, Becker CFW, Beste A, Goody RS, Ahmadian MR (2005) Monitoring the real-time kinetics of the hydrolysis reaction of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biol Chem 386: 1105–1114 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

