Par-4 inhibits Akt and suppresses Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis
- PMID: 18650932
- PMCID: PMC2519103
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.149
Par-4 inhibits Akt and suppresses Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis
Abstract
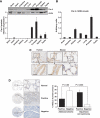
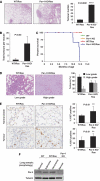
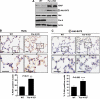
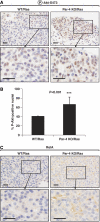
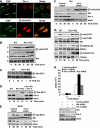
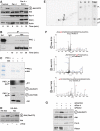
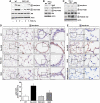
The atypical PKC-interacting protein, Par-4, inhibits cell survival and tumorigenesis in vitro, and its genetic inactivation in mice leads to reduced lifespan, enhanced benign tumour development and low-frequency carcinogenesis. Here, we demonstrate that Par-4 is highly expressed in normal lung but reduced in human lung cancer samples. We show, in a mouse model of lung tumours, that the lack of Par-4 dramatically enhances Ras-induced lung carcinoma formation in vivo, acting as a negative regulator of Akt activation. We also demonstrate in cell culture, in vivo, and in biochemical experiments that Akt regulation by Par-4 is mediated by PKCzeta, establishing a new paradigm for Akt regulation and, likely, for Ras-induced lung carcinogenesis, wherein Par-4 is a novel tumour suppressor.
Figures
References
-
- Asara JM, Christofk HR, Freimark LM, Cantley LC (2008) A label-free quantification method by MS/MS TIC compared to SILAC and spectral counting in a proteomics screen. Proteomics 8: 994–999 - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D, McCormick F, Feng J, Tsichlis P (1998) Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: the role of the PH domain. Oncogene 17: 313–325 - PubMed
-
- Bhaskar PT, Hay N (2007) The Two TORCs and Akt. Dev Cell 12: 487–502 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

