Overexpression of artemin in the tongue increases expression of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in trigeminal afferents and causes oral sensitivity to capsaicin and mustard oil
- PMID: 18652806
- PMCID: PMC2570744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.119
Overexpression of artemin in the tongue increases expression of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in trigeminal afferents and causes oral sensitivity to capsaicin and mustard oil
Abstract
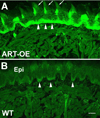
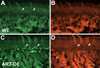
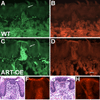
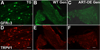
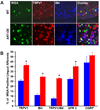
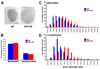
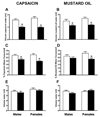
Artemin, a member of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family, supports a subpopulation of trigeminal sensory neurons through activation of the Ret/GFRalpha3 receptor tyrosine kinase complex. In a previous study we showed that artemin is increased in inflamed skin of wildtype mice and that transgenic overexpression of artemin in skin increases TRPV1 and TRPA1 expression in dorsal root ganglia neurons. In this study we examined how transgenic overexpression of artemin in tongue epithelium affects the anatomy, gene expression and calcium handling properties of trigeminal sensory afferents. At the RNA level, trigeminal ganglia of artemin overexpresser mice (ART-OEs) had an 81% increase in GFRalpha3, a 190% increase in TRPV1 and a 403% increase in TRPA1 compared to wildtype (WT) controls. Myelinated and unmyelinated fibers of the lingual nerve were increased in diameter, as was the density of GFRalpha3 and TRPV1-positive innervation to the dorsal anterior tongue and fungiform papilla. Retrograde labeling of trigeminal afferents by WGA injection into the tip of the tongue showed an increased percentage of GFRalpha3, TRPV1 and isolectin B4 afferents in ART-OE mice. ART-OE afferents had larger calcium transients in response to ligands of TRPV1 (capsaicin) and TRPA1 (mustard oil). Behavioral sensitivity was also exhibited by ART-OE mice to capsaicin and mustard oil, measured using a two-choice drinking test. These results suggest a potential role for artemin-responsive GFRalpha3/TRPV1/TRPA1 sensory afferents in mediating sensitivity associated with tissue injury, chemical sensitivity or disease states such as burning mouth syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of the neurotrophic factor artemin on sensory afferent development and sensitivity.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):565-70. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958361 Free PMC article.
-
Artemin overexpression in skin enhances expression of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in cutaneous sensory neurons and leads to behavioral sensitivity to heat and cold.J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 16;26(33):8578-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2185-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16914684 Free PMC article.
-
Artemin growth factor increases nicotinic cholinergic receptor subunit expression and activity in nociceptive sensory neurons.Mol Pain. 2014 May 22;10:31. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-10-31. Mol Pain. 2014. PMID: 24886596 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 and TRPA1 function and modulation are target tissue dependent.J Neurosci. 2011 Jul 20;31(29):10516-28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2992-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21775597 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of trigeminal chemosensation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jul;1170:184-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.03895.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19686135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous inflammatory mediators produced by injury activate TRPV1 and TRPA1 nociceptors to induce sexually dimorphic cold pain that is dependent on TRPM8 and GFRα3.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 23:2023.01.23.525238. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.23.525238. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Neurosci. 2023 Apr 12;43(15):2803-2814. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2303-22.2023. PMID: 36747719 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Characterization of sensory neuronal subtypes innervating mouse tongue.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 8;13(11):e0207069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207069. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30408082 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the melanocortin-1 receptor in acute pain and pain of inflammatory but not neuropathic origin.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 13;5(9):e12498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012498. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20856883 Free PMC article.
-
Oral cancer induced TRPV1 sensitization is mediated by PAR2 signaling in primary afferent neurons innervating the cancer microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 8;12(1):4121. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08005-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35260737 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the neurotrophic factor artemin on sensory afferent development and sensitivity.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):565-70. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW, Viswanath V, Eid SR, Petrus MJ, Earley TJ, Patapoutian A. Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron. 2004;41:849–857. - PubMed
-
- Biggs JE, Yates JM, Loescher AR, Clayton NM, Boissonade FM, Robinson PP. Changes in vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) expression following lingual nerve injury. Eur J Pain. 2007;11:192–201. - PubMed
-
- Bogen O, Dreger M, Gillen C, Schroder W, Hucho F. Identification of versican as an isolectin B4-binding glycoprotein from mammalian spinal cord tissue. Febs J. 2005;272:1090–1102. - PubMed
-
- Christianson JA, McIlwrath SL, Koerber HR, Davis BM. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1-immunopositive neurons in the mouse are more prevalent within colon afferents compared to skin and muscle afferents. Neuroscience. 2006;140:247–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

