The effects of thalidomide and minocycline on taxol-induced hyperalgesia in rats
- PMID: 18652810
- PMCID: PMC2577234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.001
The effects of thalidomide and minocycline on taxol-induced hyperalgesia in rats
Abstract
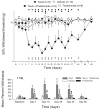
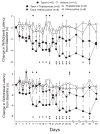
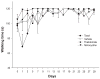
Chemotherapy-induced pain is the most common treatment-limiting complication encountered by cancer patients receiving taxane-, vinca alkaloid- or platin-based chemotherapy. Several lines of evidence indicate that activation of pro-inflammatory cascades involving the release of cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) as well as various growth factors are key events in the pathogenesis of many types of nerve-injury related pain. Similar mechanisms might also be involved in the etiology of chemotherapy-induced pain. Thalidomide and minocycline have profound immunomodulatory actions in addition to their originally intended pharmacological actions. These compounds were evaluated here for effects in preventing the development of taxol-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in rats. Thalidomide (50.0 mg/kg) reduced taxol-induced mechanical allodynia and hyperalgesia whereas minocycline (20.0 mg/kg) reduced taxol-induced mechanical hyperalgesia and allodynia as well as taxol-induced thermal hyperalgesia. These results suggest that immunomodulatory agents may provide a treatment option for the protection or reversal of chemotherapy-related pain.
Figures

References
-
- Allen JN, Moore SA, Wewers MD. Taxol enhances but does not induce interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. J Lab Clin Med. 1993;122:374–381. - PubMed
-
- Arruda JL, Sweitzer S, Rutkowski MD, DeLeo JA. Intrathecal anti-IL-6 antibody and IgG attenuates peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia in the rat: possible immune modulation in neuropathic pain1. Brain Res. 2000;879:216–225. - PubMed
-
- Bao L, Zhu Y, Elhassan AM, Wu Q, Xiao B, Zhu J, Lindgren JU. Adjuvant-induced arthritis: IL-1 beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha are up- regulated in the spinal cord. Neuroreport. 2001;12:3905–3908. - PubMed
-
- Barnhill RL, Doll J, Millikan LE, Hastings RC. Studies on the anti-inflammatory properties of thalidomide: Effects on polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Amer Acad Dermatol. 1984;11:814–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

