Experimental approaches for the study of oxytocin and vasopressin gene expression in the central nervous system
- PMID: 18655870
- PMCID: PMC5079141
- DOI: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00404-4
Experimental approaches for the study of oxytocin and vasopressin gene expression in the central nervous system
Abstract
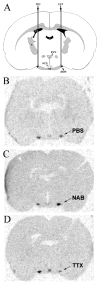
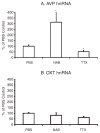
Intron-specific probes measure heteronuclear RNA (hnRNA) levels and thus approximate the transcription rates of genes, in part because of the rapid turnover of this intermediate form of RNA in the cell nucleus. Previously, we used oxytocin (Oxt)- and vasopressin (Avp)- intron-specific riboprobes to measure changes in Oxt and Avp hnRNA levels in the supraoptic nucleus (SON) by quantitative in situ hybridization (ISH) after various classical physiological perturbations, including acute and chronic salt loading, and lactation. In the present experiments, we used a novel experimental model to study the neurotransmitter regulation of Oxt and Avp gene expression in the rat SON in vivo. Bilateral cannulae connected via tubing to Alzet osmotic mini-pumps were positioned over the SON. In every experiment, one SON was infused with PBS and served as the control SON in each animal, and the contralateral SON received infusions of various neurotransmitter agonists and antagonists. Using this approach, we found that Avp but not Oxt gene expression increased after acute (2-5h) combined excitatory amino acid agonist and GABA antagonist treatment, similar to what we found after an acute hyperosmotic stimulus. Since both OXT and AVP are known to be comparably and robustly secreted in response to acute osmotic stimuli in vivo and glutamate agonists in vitro, our results indicate a dissociation between OXT secretion and Oxt gene transcription in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential kinetics of oxytocin and vasopressin heteronuclear RNA expression in the rat supraoptic nucleus in response to chronic salt loading in vivo.J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Feb;20(2):227-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2007.01640.x. Epub 2007 Dec 14. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18088359
-
Studies of oxytocin and vasopressin gene expression in the rat hypothalamus using exon- and intron-specific probes.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006 May;290(5):R1233-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00709.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 15. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16357095
-
Specific expression of an oxytocin-enhanced cyan fluorescent protein fusion transgene in the rat hypothalamus and posterior pituitary.J Endocrinol. 2010 Mar;204(3):275-85. doi: 10.1677/JOE-09-0289. Epub 2009 Dec 21. J Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20026620 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression in the supraoptic nucleus.Microsc Res Tech. 2002 Jan 15;56(2):158-63. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10020. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 11810718 Review.
-
Estrogen modulates oxytocin gene expression in regions of the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei that contain estrogen receptor-beta.Prog Brain Res. 2002;139:15-29. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)39004-6. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12436923 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotransmitter regulation of c-fos and vasopressin gene expression in the rat supraoptic nucleus.Exp Neurol. 2009 Sep;219(1):212-22. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.05.019. Epub 2009 May 20. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19463813 Free PMC article.
-
Salt appetite is reduced by a single experience of drinking hypertonic saline in the adult rat.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 11;9(8):e104802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104802. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25111786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arima H, Kondo K, Kakiya S, Nagasaki H, Yokoi H, Yambe Y, Murase T, Iwasaki Y, Oiso Y. Rapid and sensitive vasopressin heteronuclear RNA responses to changes in plasma osmolality. J Neuroendocrinol. 1999;11:337–341. - PubMed
-
- Bourque CW, Richard D. Axonal projections from the organum vasculosum lamina terminalis to the supraoptic nucleus: functional analysis and presynaptic modulation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001;28:570–574. - PubMed
-
- Brooks PJ, Kaplitt MG, Kleopoulos SP, Funabashi T, Mobbs CV, Pfaff DW. Detection of messenger RNA and low-abundance heteronuclear RNA with single-stranded DNA probes produced by amplified primer extension labeling. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993;41:1761–1766. - PubMed
-
- Burbach JP, Luckman SM, Murphy D, Gainer H. Gene regulation in the magnocellular hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:1197–1267. - PubMed
-
- Fremeau RT, Jr, Autelitano DJ, Blum M, Wilcox J, Roberts JL. Intervening sequence-specific in situ hybridization: detection of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene primary transcript in individual neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989;6:197–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

