uPA impairs cerebrovasodilation after hypoxia/ischemia through LRP and ERK MAPK
- PMID: 18656457
- PMCID: PMC2572778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.115
uPA impairs cerebrovasodilation after hypoxia/ischemia through LRP and ERK MAPK
Abstract
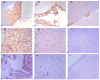
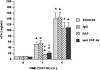
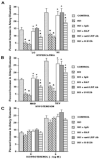
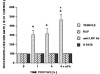
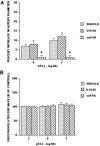
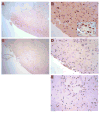
We have previously observed that soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) prevents impairment of cerebrovasodilation induced by hypercapnia and hypotension after hypoxia/ischemia (H/I) in the newborn pig. In this study, we investigated the role of low-density lipoprotein-related protein (LRP) receptor and the ERK isoform of mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) in uPA-mediated impairment of vasodilation after H/I in piglets equipped with a closed cranial window. CSF uPA increased from 9+/-2 to 52+/-8 and 140+/-21 ng/ml at 1 and 4 h after H/I, respectively. The LRP antagonist receptor associated protein (RAP) and anti-LRP antibody blunted the increase in CSF uPA at 1 h (17+/-2 ng/ml) but not 4 h post insult. uPA detectable in sham-treated cortex by immunohistochemistry was markedly elevated 4 h after H/I. Phosphorylation (activation) of CSF ERK MAPK was detected at 1 and 4 h post H/I and blocked by RAP. Exogenous uPA administered at 4 h post H/I further stimulated ERK MAPK phosphorylation, which was blocked by RAP. Pre-treatment of piglets with RAP, anti-LRP, and suPAR completely prevented, and the ERK MAPK antagonist U 0126 partially prevented, impaired responses to hypotension and hypercapnia post H/I, but none of these antagonists affected the response to isoproterenol. These data indicate that uPA is upregulated after H/I through an LRP-dependent process and that the released uPA impairs hypercapnic and hypotensive dilation through an LRP- and ERK MAPK dependent pathway. These data suggest that modulation of uPA upregulation and/or uPA-mediated signal transduction may preserve cerebrohemodynamic control after hypoxia/ischemia.
Figures
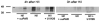
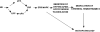
References
-
- Armstead WM. NOC/oFQ and NMDA contribute to piglet hypoxic ischemic hypotensive cerebrovasodilation impairment. Pediatr Res. 2002;51:586–591. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Cines DB, Higazi AA. Plasminogen activators contribute to impairment of hypercapnic and hypotensive cerebrovasodilation after cerebral hypoxia/ischemia in the newborn pig. Stroke. 2005;36:2265–2269. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Cines DB, Higazi AA. Plasminogen activators contribute to age dependent impairment of NMDA cerebrovasodilation after brain injury. Dev Brain Res. 2005;156:139–146. - PubMed
-
- Bdeir K, Murciano JC, Tomaszewski J, Koniaris L, Martinez J, Cines DB, Muzykantov VR, Higazi AA. Uorkinase mediates fibrinolysis in the pulmonary microvasculature. Blood. 2000;96:1820–1826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL 81864/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083121/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 76206/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS 53410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL076406/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 83121/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL081864/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD 57355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL 82545/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076206/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS053410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 77760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 76406/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 07971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

