Resolving crossings in the corticospinal tract by two-tensor streamline tractography: Method and clinical assessment using fMRI
- PMID: 18657622
- PMCID: PMC2746909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.06.034
Resolving crossings in the corticospinal tract by two-tensor streamline tractography: Method and clinical assessment using fMRI
Abstract
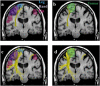
An inherent drawback of the traditional diffusion tensor model is its limited ability to provide detailed information about multidirectional fiber architecture within a voxel. This leads to erroneous fiber tractography results in locations where fiber bundles cross each other. This may lead to the inability to visualize clinically important tracts such as the lateral projections of the corticospinal tract. In this report, we present a deterministic two-tensor eXtended Streamline Tractography (XST) technique, which successfully traces through regions of crossing fibers. We evaluated the method on simulated and in vivo human brain data, comparing the results with the traditional single-tensor and with a probabilistic tractography technique. By tracing the corticospinal tract and correlating with fMRI-determined motor cortex in both healthy subjects and patients with brain tumors, we demonstrate that two-tensor deterministic streamline tractography can accurately identify fiber bundles consistent with anatomy and previously not detected by conventional single-tensor tractography. When compared to the dense connectivity maps generated by probabilistic tractography, the method is computationally efficient and generates discrete geometric pathways that are simple to visualize and clinically useful. Detection of crossing white matter pathways can improve neurosurgical visualization of functionally relevant white matter areas.
Figures
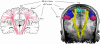



References
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 1974;19:716–723.
-
- Alexander AL, Hasan KM, Lazar M, Tsuruda JS, Parker DL. Analysis of partial volume effects in diffusion-tensor MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2001;45:770–780. - PubMed
-
- Alexander DC. Multiple-Fiber Reconstruction Algorithms for Diffusion MRI. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2005;1046:113–133. - PubMed
-
- Alexander DC, Barker GJ, Arridge SR. Detection and modeling of non-Gaussian apparent diffusion coefficient profiles in human brain data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;48:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR in Biomedicine. 1995;8:333–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

