Potential role of high-mobility group box 1 in cystic fibrosis airway disease
- PMID: 18658107
- PMCID: PMC2566793
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200712-1894OC
Potential role of high-mobility group box 1 in cystic fibrosis airway disease
Abstract
Rationale: High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a potent inflammatory mediator elevated in sepsis and rheumatoid arthritis, although its role in cystic fibrosis (CF) lung disease is unknown.
Objectives: To determine whether HMGB1 contributes to CF lung inflammation, including neutrophil chemotaxis and lung matrix degradation.
Methods: We used sputum and serum from subjects with CF and a Scnn1b-transgenic (Scnn1b-Tg) mouse model that overexpresses beta-epithelial Na(+) channel in airways and mimics the CF phenotype, including lung inflammation. Human secretions and murine bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was assayed for HMGB1 by Western blot and ELISA. Neutrophil chemotaxis was measured in vitro after incubation with human neutrophils. The collagen fragment proline-glycine-proline (PGP) was measured by tandem mass spectroscopy.
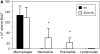
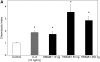
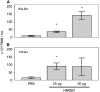
Measurements and main results: HMGB1 was detected in CF sputum at higher levels than secretions from normal individuals. Scnn1b-Tg mice had elevated levels of HMGB1 by Western blot and ELISA. We demonstrated that dose-dependent chemotaxis of human neutrophils stimulated by purified HMGB1 was partially dependent on CXC chemokine receptors and that this could be duplicated in CF sputum and BALF from Scnn1b-Tg mice. Neutralization by anti-HMGB1 antibody, in both the sputum and BALF-reduced chemotaxis, which suggested that HMGB1 contributed to the chemotactic properties of these samples. Intratracheal administration of purified HMGB1 induced neutrophil influx into the airways of mice and promoted the release of PGP. PGP was also elevated in Scnn1b-Tg mice and CF serum.
Conclusions: HMGB1 expression contributes to pulmonary inflammation and lung matrix degradation in CF airway disease and deserves further investigation as a biomarker and potential therapeutic target.
Figures












References
-
- Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 1999;285:248–251. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey KJ. HMG-1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 2000;165:2950–2954. - PubMed
-
- Kim JY, Park JS, Strassheim D, Douglas I, Diaz del Valle F, Asehnoune K, Mitra S, Kwak SH, Yamada S, Maruyama I, et al. HMGB1 contributes to the development of acute lung injury after hemorrhage. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2005;288:L958–L965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50GM049222/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL068743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA13148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL090999/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090999/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM049222/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL077783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23DK075788-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01HL068743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P30DK072482-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK075788/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

