DNA supercoiling inhibits DNA knotting
- PMID: 18658246
- PMCID: PMC2528182
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn467
DNA supercoiling inhibits DNA knotting
Abstract
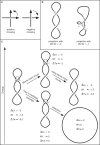
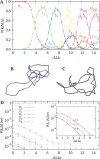
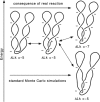
Despite the fact that in living cells DNA molecules are long and highly crowded, they are rarely knotted. DNA knotting interferes with the normal functioning of the DNA and, therefore, molecular mechanisms evolved that maintain the knotting and catenation level below that which would be achieved if the DNA segments could pass randomly through each other. Biochemical experiments with torsionally relaxed DNA demonstrated earlier that type II DNA topoisomerases that permit inter- and intramolecular passages between segments of DNA molecules use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to select passages that lead to unknotting rather than to the formation of knots. Using numerical simulations, we identify here another mechanism by which topoisomerases can keep the knotting level low. We observe that DNA supercoiling, such as found in bacterial cells, creates a situation where intramolecular passages leading to knotting are opposed by the free-energy change connected to transitions from unknotted to knotted circular DNA molecules.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Closing the DNA replication cycle: from simple circular molecules to supercoiled and knotted DNA catenanes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Aug 22;47(14):7182-7198. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz586. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31276584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tightening of DNA knots by supercoiling facilitates their unknotting by type II DNA topoisomerases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 1;108(9):3608-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016150108. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21321228 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of supercoils in nicked and gapped DNA drives DNA unknotting and postreplicative decatenation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 3;43(15):7229-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv683. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26150424 Free PMC article.
-
DNA supercoiling and its role in DNA decatenation and unknotting.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Apr;38(7):2119-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1161. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20026582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetic proofreading can explain the supression of supercoiling of circular DNA molecules by type-II topoisomerases.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2001 Mar;63(3 Pt 1):031909. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.63.031909. Epub 2001 Feb 27. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2001. PMID: 11308680
Cited by
-
Kinetic pathways of topology simplification by Type-II topoisomerases in knotted supercoiled DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 10;47(1):69-84. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1174. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30476194 Free PMC article.
-
How do type II topoisomerases use ATP hydrolysis to simplify DNA topology beyond equilibrium? Investigating the relaxation reaction of nonsupercoiling type II topoisomerases.J Mol Biol. 2009 Feb 6;385(5):1397-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.11.056. Epub 2008 Dec 7. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19094994 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient deformation algorithm for plasmid DNA simulations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Sep 15;15(1):301. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-301. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 25225011 Free PMC article.
-
Closing the DNA replication cycle: from simple circular molecules to supercoiled and knotted DNA catenanes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Aug 22;47(14):7182-7198. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz586. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31276584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Models that include supercoiling of topological domains reproduce several known features of interphase chromosomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Mar;42(5):2848-55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1353. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24366878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang JC. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Bates AD, Maxwell A. Energy coupling in type II topoisomerases: why do they hydrolyze ATP? Biochemistry. 2007;46:7929–7941. - PubMed
-
- Rybenkov VV, Ullsperger C, Vologodskii AV, Cozzarelli NR. Simplification of DNA topology below equilibrium values by type II topoisomerases. Science. 1997;277:690–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

