Escherichia coli constructs expressing human or porcine enterotoxins induce identical diarrheal diseases in a piglet infection model
- PMID: 18658289
- PMCID: PMC2547035
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00893-08
Escherichia coli constructs expressing human or porcine enterotoxins induce identical diarrheal diseases in a piglet infection model
Abstract
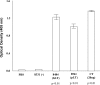
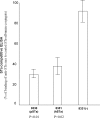
To develop a piglet model for studying diarrheal disease and developing vaccines, we challenged gnotobiotic piglets with isogenic Escherichia coli strains constructed to express porcine 987P(F6) fimbriae and a heat-labile or a heat-stable enterotoxin to examine clinical outcomes. Piglets developed identical diarrheal diseases when inoculated with constructs expressing human or porcine enterotoxins.
Figures


References
-
- Baker, D. R., L. O. Billey, and D. H. Francis. 1996. Distribution of K88 Escherichia coli-adhesive and nonadhesive phenotypes among pigs of four breeds. Vet. Microbiol. 54:123-132. - PubMed
-
- Berberov, E. M., Y. Zhou, D. H. Francis, M. A. Scott, S. D. Kachman, and R. A. Moxley. 2004. Relative importance of heat-labile enterotoxin in the causation of severe diarrheal disease in the gnotobiotic piglet model by a strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli that produces multiple enterotoxins. Infect. Immun. 72:3914-3924. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

