TGFbeta in Cancer
- PMID: 18662538
- PMCID: PMC3512574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.001
TGFbeta in Cancer
Abstract
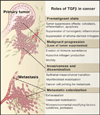
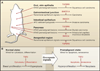
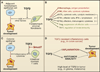
The transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) signaling pathway is a key player in metazoan biology, and its misregulation can result in tumor development. The regulatory cytokine TGFbeta exerts tumor-suppressive effects that cancer cells must elude for malignant evolution. Yet, paradoxically, TGFbeta also modulates processes such as cell invasion, immune regulation, and microenvironment modification that cancer cells may exploit to their advantage. Consequently, the output of a TGFbeta response is highly contextual throughout development, across different tissues, and also in cancer. The mechanistic basis and clinical relevance of TGFbeta's role in cancer is becoming increasingly clear, paving the way for a better understanding of the complexity and therapeutic potential of this pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, Brennan C, Lahti-Domenici J, Huang H, Porter D, Hu M, Chin L, Richardson A, et al. Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:17–32. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL. Inhibition of TGFbeta signaling in cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006;16:30–37. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft GS, Yang X, Glick AB, Weinstein M, Letterio JL, Mizel DE, Anzano M, Greenwell-Wild T, Wahl SM, Deng C, Roberts AB. Mice lacking Smad3 show accelerated wound healing and an impaired local inflammatory response. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999;1:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Becker C, Fantini MC, Neurath MF. TGF-beta as a T cell regulator in colitis and colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006;17:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

