DNA organization by the apicoplast-targeted bacterial histone-like protein of Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 18663012
- PMCID: PMC2528193
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn483
DNA organization by the apicoplast-targeted bacterial histone-like protein of Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
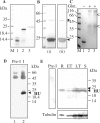
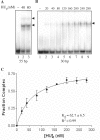
Apicomplexans, including the pathogens Plasmodium and Toxoplasma, carry a nonphotosynthetic plastid of secondary endosymbiotic origin called the apicoplast. The P. falciparum apicoplast contains a 35 kb, circular DNA genome with limited coding capacity that lacks genes encoding proteins for DNA organization and replication. We report identification of a nuclear-encoded bacterial histone-like protein (PfHU) involved in DNA compaction in the apicoplast. PfHU is associated with apicoplast DNA and is expressed throughout the parasite's intra-erythocytic cycle. The protein binds DNA in a sequence nonspecific manner with a minimum binding site length of approximately 27 bp and a K(d) of approximately 63 nM and displays a preference for supercoiled DNA. PfHU is capable of condensing Escherichia coli nucleoids in vivo indicating its role in DNA compaction. The unique 42 aa C-terminal extension of PfHU influences its DNA condensation properties. In contrast to bacterial HUs that bend DNA, PfHU promotes concatenation of linear DNA and inhibits DNA circularization. Atomic Force Microscopic study of PfHU-DNA complexes shows protein concentration-dependent DNA stiffening, intermolecular bundling and formation of DNA bridges followed by assembly of condensed DNA networks. Our results provide the first functional characterization of an apicomplexan HU protein and provide additional evidence for red algal ancestry of the apicoplast.
Figures






References
-
- Wilson RJM. Progress with parasite plastids. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;319:257–274. (Iain) - PubMed
-
- Foth BJ, McFadden GI. The apicoplast: a plastid in Plasmodium falciparum and other apicomplexan parasites. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2003;224:57–110. - PubMed
-
- Wilson RJM. Parasite plastids: approaching the endgame. Biol. Rev. 2005;80:129–153. (Iain) - PubMed
-
- Fichera ME, Roos DS. A plastid organelle as a drug target in apicomplexan parasites. Nature. 1997;390:407–409. - PubMed
-
- Gardner MJ, Williamson DH, Wilson RJM. A circular DNA molecule in malaria parasites encodes an RNA polymerase like that of prokaryotes and chloroplasts. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1991;44:115–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

