Menopause and the metabolic syndrome: the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation
- PMID: 18663170
- PMCID: PMC2894539
- DOI: 10.1001/archinte.168.14.1568
Menopause and the metabolic syndrome: the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation
Abstract
Background: Cross-sectional studies suggest that prevalence of the metabolic syndrome (MetS) increases from premenopause to postmenopause in women, independent of age. Little is known about why. We hypothesized that the incidence of the MetS increases with progression through menopause and that this increase is explained by the progressive androgenicity of the hormonal milieu.
Methods: This longitudinal, 9-year study of 949 participants in the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation investigates the natural history of the menopausal transition. Participants of 5 ethnicities at 7 geographic sites were recruited when they were premenopausal or early perimenopausal and were eligible for this study if they (1) reached menopause during the study; (2) had never taken hormone therapy, and (3) did not have diabetes mellitus or the MetS at baseline. The primary outcome was the presence of MetS using National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. Secondary outcomes were the components of the MetS.
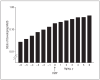
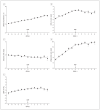
Results: By the final menstrual period, 13.7% of the women had new-onset MetS. Longitudinal analyses, centered at the final menstrual period, were adjusted for age at menopause, ethnicity, study site, marital status, education, body mass index, smoking, and aging. Odds of developing the MetS per year in perimenopause were 1.45 (95% confidence interval, 1.35-1.56); after menopause, 1.24 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.30). These odds were significantly different (P < .001). An increase in bioavailable testosterone or a decrease in sex hormone-binding globulin levels increased the odds.
Conclusions: As testosterone progressively dominates the hormonal milieu during the menopausal transition, the prevalence of MetS increases, independent of aging and other important covariates. This may be a pathway by which cardiovascular disease increases during menopause.
Figures
References
-
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285(19):2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002;287(3):356–359. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115(5):e69–e171. published correction appears in Circulation. 2007;115(5):e172. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.179918. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB. Metabolic risk factors for coronary heart disease in women: perspective from the Framingham Study. Am Heart J. 1987;114(2):413–419. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Hjortland MC, McNamara PM, Gordon T. Menopause and risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85(4):447–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG012553/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012554/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012539/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012531/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NR004061/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012554/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012553/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NR004061/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012539/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012531/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

