Use of statins and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment without dementia in a cohort study
- PMID: 18663180
- PMCID: PMC2676946
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000319647.15752.7b
Use of statins and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment without dementia in a cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Evidence of a relation between use of lipid lowering drugs and cognitive outcomes is mixed. This study aimed to test the association between use of statins and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment without dementia (CIND) over 5 years of follow-up.
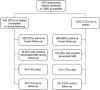
Methods: Data were from a population-based cohort study comprising 1,789 older Mexican Americans. All participants had cognitive and clinical evaluations performed every 12 to 15 months. Participants who fell below specified cutpoints on cognitive tests were then evaluated clinically. Dementia diagnoses were finalized by an adjudication team. A total of 1,674 participants free of dementia/CIND at baseline were included in these analyses. Statin use was verified at each participant's home by medicine cabinet inspection. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate the association between statin use and incidence of dementia/CIND.
Results: Overall, 452 of 1,674 participants (27%) took statins at any time during the study. Over the 5-year follow-up period, 130 participants developed dementia/CIND. In Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for education, smoking status, presence of at least one APOE epsilon4 allele, and history of stroke or diabetes at baseline, persons who had used statins were about half as likely as those who did not use statins to develop dementia/CIND (HR = 0.52; 95% CI 0.34, 0.80).
Conclusion: Statin users were less likely to have incident dementia/cognitive impairment without dementia during a 5-year follow-up. These results add to the emerging evidence suggesting a protective effect of statin use on cognitive outcomes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Use of statins and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment without dementia in a cohort study.Neurology. 2009 Mar 31;72(13):1190-1. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000346461.00520.28. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19332702 No abstract available.
-
Use of statins and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment without dementia in a cohort study.Neurology. 2009 Aug 4;73(5):406; author reply 406-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ab966f. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19652149 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Use of statins and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment without dementia in a cohort study.Neurology. 2009 Aug 4;73(5):406; author reply 406-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ab966f. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19652149 No abstract available.
-
Statins, incident Alzheimer disease, change in cognitive function, and neuropathology.Neurology. 2008 May 6;70(19 Pt 2):1795-802. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000288181.00826.63. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Neurology. 2008. PMID: 18199831
-
Statins and cognitive function in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study.Neurology. 2005 Nov 8;65(9):1388-94. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000182897.18229.ec. Neurology. 2005. PMID: 16275825
-
Association of blood lipids, atherosclerosis and statin use with dementia and cognitive impairment after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Jan;57:100962. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100962. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31505259
-
The risk of dementia in relation to statins and other lipid lowering agents.Neurol Res. 2003 Sep;25(6):601-4. doi: 10.1179/016164103101202039. Neurol Res. 2003. PMID: 14503013 Review.
Cited by
-
KIF6 719Arg allele is associated with statin effects on cholesterol levels in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease patients.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(1):111-6. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-121015. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 22914592 Free PMC article.
-
Emulating a target trial of statin use and risk of dementia using cohort data.Neurology. 2020 Sep 8;95(10):e1322-e1332. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010433. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32753444 Free PMC article.
-
β-sitosterol inhibits high cholesterol-induced platelet β-amyloid release.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2011 Dec;43(6):691-7. doi: 10.1007/s10863-011-9383-2. Epub 2011 Oct 4. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2011. PMID: 21969169
-
The role of statins in dementia or Alzheimer's disease incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 3;16:1473796. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1473796. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39963242 Free PMC article.
-
Age-varying association between statin use and incident Alzheimer's disease.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010 Jul;58(7):1311-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02906.x. Epub 2010 Jun 1. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010. PMID: 20533968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freeman D, Norrie J, Sattar N, et al. Pravastatin and the development of diabetes mellitus: evidence for a protective treatment effect in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study. Circulation 2001;103:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Keech A, Colquhoun D, Best J, et al. Secondary prevention of cardiovascular events with long-term pravastatin in patients with diabetes or impaired fasting glucose. Results from the LIPID trial. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2713–2721. - PubMed
-
- Sever P, Dahlof B, Poulter N, et al. Prevention of coronary and stroke events with atorvastatin in hypertensive patients who have average or lower than average cholesterol concentrations in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Lipid Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2003;361:1149–1158. - PubMed
-
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin in 5963 people with diabetes: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003;361:2005–2016. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd J, Blauw G, Murphy MB. Pravastatin in elderly individuals at risk of vascular disease (PROSPER): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002;360:1623–1630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous