PCSK9 function and physiology
- PMID: 18663786
- PMCID: PMC3837453
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.cx00001-jlr200
PCSK9 function and physiology
Abstract
PCSK9 has exploded onto center stage plasma cholesterol metabolism, raising hopes for a new strategy to treat hypercholesterolemia. PCSK9 in a plasma protein that triggers increased degradation of the LDL receptor. Gain-of-function mutations in PCSK9 reduce LDL receptor levels in the liver, resulting in high levels of LDL cholesterol in the plasma and increased susceptibility to coronary heart disease. Loss-of-function mutations lead to higher levels of the LDL receptor, lower LDL cholesterol levels and protection from coronary heart disease. Two papers in this issue of the Journal of Lipid Research exemplify the rapid pace of progress in understanding PCSK9 molecular interactions and physiology. Dr. Shilpa Pandit and coworkers from Merck Research Laboratories describe the functional basis for the hypercholesterolemia associated with gain-of-function missense mutations in PCSK9. Dr. Jay Horton's group at UT Southwestern describe the kinetics and metabolism of PCSK9 and the impact of PCSK9 on LDL receptors in the liver and adrenal gland.
Figures
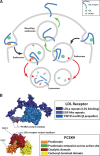
Comment on
-
Functional analysis of sites within PCSK9 responsible for hypercholesterolemia.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jun;49(6):1333-43. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800049-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 19. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18354137
-
Plasma PCSK9 preferentially reduces liver LDL receptors in mice.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jun;49(6):1303-11. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800027-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 19. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18354138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park SW, Moon YA, Horton JD. Post-transcriptional regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor protein by proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9a in mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:50630–50638. - PubMed
-
- Benjannet S, Rhainds D, Essalmani R, Mayne J, Wickham L, Jin W, Asselin MC, Hamelin J, Varret M, Allard D, et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:48865–48875. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

