Adjuvant oral clodronate improves the overall survival of primary breast cancer patients with micrometastases to the bone marrow: a long-term follow-up
- PMID: 18664560
- PMCID: PMC2733118
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdn429
Adjuvant oral clodronate improves the overall survival of primary breast cancer patients with micrometastases to the bone marrow: a long-term follow-up
Abstract
Background: Adding oral clodronate to postoperative adjuvant breast cancer therapy significantly improves disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). Long-term follow-up data from the prospective, randomized, controlled study are reported.
Patients and methods: Patients with primary breast cancer received clodronate 1600 mg/day for 2 years or no treatment along with standard adjuvant breast cancer treatment.
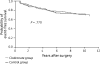
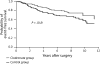
Results: Analysis of 290 of 302 patients demonstrated that a significant improvement in OS was maintained in the clodronate group at a median follow-up of 103 +/- 12 months; 20.4% of patients in the clodronate group versus 40.7% of control group patients (P = 0.04) died during the 8.5 years following primary surgical therapy. Significant reductions in the incidence of bony and visceral metastases and improvement in duration of DFS at 36- and 55-month follow-up periods were no longer seen with clodronate.
Conclusion: These long-term survival data extend the survival advantage reported in previous studies with oral clodronate in breast cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reduction in bone relapse and improved survival with oral clodronate for adjuvant treatment of operable breast cancer [ISRCTN83688026].Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8(2):R13. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Breast Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16542503 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral sodium clodronate for nonmetastatic prostate cancer--results of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial: Medical Research Council PR04 (ISRCTN61384873).J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007 May 16;99(10):765-76. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk178. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007. PMID: 17505072 Clinical Trial.
-
Adjuvant therapy with oral sodium clodronate in locally advanced and metastatic prostate cancer: long-term overall survival results from the MRC PR04 and PR05 randomised controlled trials.Lancet Oncol. 2009 Sep;10(9):872-6. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70201-3. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Lancet Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19674936 Free PMC article.
-
Oral bisphosphonates as adjuvant therapy for operable breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 15;12(20 Pt 2):6301s-6304s. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1211. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17062718 Review.
-
Should oral bisphosphonates be standard of care in women with early breast cancer?Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005 Apr;90(3):315-8. doi: 10.1007/s10549-004-4259-3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005. PMID: 15830146 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone microenvironment-mediated resistance of cancer cells to bisphosphonates and impact on bone osteocytes/stem cells.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016 Aug;33(6):563-88. doi: 10.1007/s10585-016-9798-6. Epub 2016 May 7. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016. PMID: 27155840
-
Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Jun;9(6):447-64. doi: 10.1038/nrd3137. Epub 2010 May 14. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20467424 Review.
-
Basic research and clinical applications of bisphosphonates in bone disease: what have we learned over the last 40 years?J Transl Med. 2013 Dec 11;11:303. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-303. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 24330728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of zoledronic acid on disseminated tumor cells in bone marrow and survival: results of a prospective clinical trial.BMC Cancer. 2013 Oct 15;13:480. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-480. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24128322 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Targeted and Osteo-Oncologic Treatment in Early Breast Cancer: What Is State-of-the-Art and What Might Become so within the Next 5 Years?Breast Care (Basel). 2014 Jul;9(3):161-7. doi: 10.1159/000365129. Breast Care (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25177257 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts and Figures, 2003–2004. American Cancer Society Inc.; 2003. . American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA, USA.
-
- Ferlay J, Bray P, Pisani P, Parkin DM. GLOBOCAN 2002: Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide. IARC CancerBase No. 5. Version 2.0. IARC Press; 2004.
-
- McCloskey EV, Guest JF, Kanis JA. The clinical and cost considerations of bisphosphonates in preventing bone complications in patients with metastatic breast cancer or multiple myeloma. Drugs. 2001;61:1253–1274. - PubMed
-
- Paterson AH. The role of adjuvant therapy with bisphosphonates in cancer. Am J Cancer. 2004;3:25–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

