Acute hypertonicity alters aquaporin-2 trafficking and induces a MAPK-dependent accumulation at the plasma membrane of renal epithelial cells
- PMID: 18664568
- PMCID: PMC2546545
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801071200
Acute hypertonicity alters aquaporin-2 trafficking and induces a MAPK-dependent accumulation at the plasma membrane of renal epithelial cells
Abstract
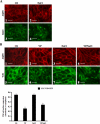
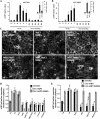
The unique phenotype of renal medullary cells allows them to survive and functionally adapt to changes of interstitial osmolality/tonicity. We investigated the effects of acute hypertonic challenge on AQP2 (aquaporin-2) water channel trafficking. In the absence of vasopressin, hypertonicity alone induced rapid (<10 min) plasma membrane accumulation of AQP2 in rat kidney collecting duct principal cells in situ, and in several kidney epithelial lines. Confocal microscopy revealed that AQP2 also accumulated in the trans-Golgi network (TGN) following hypertonic challenge. AQP2 mutants that mimic the Ser(256)-phosphorylated and -nonphosphorylated state accumulated at the cell surface and TGN, respectively. Hypertonicity did not induce a change in cytosolic cAMP concentration, but inhibition of either calmodulin or cAMP-dependent protein kinase A activity blunted the hypertonicity-induced increase of AQP2 cell surface expression. Hypertonicity increased p38, ERK1/2, and JNK MAPK activity. Inhibiting MAPK activity abolished hypertonicity-induced accumulation of AQP2 at the cell surface but did not affect either vasopressin-dependent AQP2 trafficking or hypertonicity-induced AQP2 accumulation in the TGN. Finally, increased AQP2 cell surface expression induced by hypertonicity largely resulted from a reduction in endocytosis but not from an increase in exocytosis. These data indicate that acute hypertonicity profoundly alters AQP2 trafficking and that hypertonicity-induced AQP2 accumulation at the cell surface depends on MAP kinase activity. This may have important implications on adaptational processes governing transcellular water flux and/or cell survival under extreme conditions of hypertonicity.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Psychotropic drugs upregulate aquaporin-2 via vasopressin-2 receptor/cAMP/protein kinase A signaling in inner medullary collecting duct cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):F963-F971. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00576.2020. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33843270
-
Vasopressin-stimulated increase in phosphorylation at Ser269 potentiates plasma membrane retention of aquaporin-2.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):24617-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803074200. Epub 2008 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18606813 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Poria cocos on hypertonic stress-induced water channel expression and apoptosis in renal collecting duct cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 May 7;141(1):368-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.02.048. Epub 2012 Mar 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22414475
-
Regulation of aquaporin-2 trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(190):133-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79885-9_6. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19096775 Review.
-
Aquaporin 2 regulation: implications for water balance and polycystic kidney diseases.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Nov;17(11):765-781. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00447-x. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34211154 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypertonic stress promotes autophagy and microtubule-dependent autophagosomal clusters.Autophagy. 2013 Apr;9(4):550-67. doi: 10.4161/auto.23662. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Autophagy. 2013. PMID: 23380587 Free PMC article.
-
Cell biology of vasopressin-regulated aquaporin-2 trafficking.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Aug;464(2):133-44. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1129-4. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 22744229 Review.
-
The Raf kinase inhibitor PLX5568 slows cyst proliferation in rat polycystic kidney disease but promotes renal and hepatic fibrosis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Nov;26(11):3458-65. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr432. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21804086 Free PMC article.
-
AT1a receptor knockout in mice impairs urine concentration by reducing basal vasopressin levels and its receptor signaling proteins in the inner medulla.Kidney Int. 2009 Jul;76(2):169-77. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.134. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19387470 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB modulates aquaporin-2 transcription in renal collecting duct principal cells.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 17;283(42):28095-105. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708350200. Epub 2008 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18703515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Hoek, A., Huang, Y., and Fang, P. (2001) in Protein Adaptations and Signal Transduction, pp. 73-85, Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam
-
- Di Ciano-Oliveira, C., Thirone, A. C., Szaszi, K., and Kapus, A. (2006) Acta Physiol. (Oxford) 187 257-272 - PubMed
-
- Nasuhoglu, C., Feng, S., Mao, Y., Shammat, I., Yamamato, M., Earnest, S., Lemmon, M., and Hilgemann, D. W. (2002) Am. J. Physiol. 283 C223-C234 - PubMed
-
- Rehn, M., Weber, W. M., and Clauss, W. (1998) Pflugers Arch. 436 270-279 - PubMed
-
- Sheikh-Hamad, D., and Gustin, M. C. (2004) Am. J. Physiol. 287 F1102-F1110 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

