Adaptations in pulsatile insulin secretion, hepatic insulin clearance, and beta-cell mass to age-related insulin resistance in rats
- PMID: 18664594
- PMCID: PMC2575907
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90451.2008
Adaptations in pulsatile insulin secretion, hepatic insulin clearance, and beta-cell mass to age-related insulin resistance in rats
Abstract
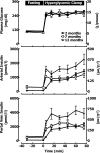
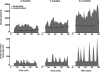
In health insulin is secreted in discrete insulin secretory bursts from pancreatic beta-cells, collectively referred to as beta-cell mass. We sought to establish the relationship between beta-cell mass, insulin secretory-burst mass, and hepatic insulin clearance over a range of age-related insulin sensitivity in adult rats. To address this, we used a novel rat model with chronically implanted portal vein catheters in which we recently established the parameters to permit deconvolution of portal vein insulin concentration profiles to measure insulin secretion and resolve its pulsatile components. In the present study, we examined total and pulsatile insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, hepatic insulin clearance, and beta-cell mass in 35 rats aged 2-12 mo. With aging, insulin sensitivity declined, but euglycemia was sustained by an adaptive increase in fasting and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through the mechanism of a selective augmentation of insulin pulse mass. The latter was attributable to a closely related increase in beta-cell mass (r=0.8, P<0.001). Hepatic insulin clearance increased with increasing portal vein insulin pulse amplitude, damping the delivery of insulin in the systemic circulation. In consequence, the curvilinear relationship previously reported between insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity was extended to both insulin pulse mass and beta-cell mass vs. insulin sensitivity. These data support a central role of adaptive changes in beta-cell mass to permit appropriate insulin secretion in the setting of decreasing insulin sensitivity in the aging animal. They emphasize the cooperative role of pancreatic beta-cells and the liver in regulating the secretion and delivery of insulin to the systemic circulation.
Figures

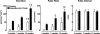
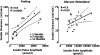


References
-
- Ahren B, Pacini G. Age-related reduction in glucose elimination is accompanied by reduced glucose effectiveness and increased hepatic insulin extraction in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 3350–3356, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Backer JM, Kahn CR, Cahill DA, Ullrich A, White MF. Receptor-mediated internalization of insulin requires a 12-amino acid sequence in the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor β-subunit. J Biol Chem 265: 16450–16454, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Barzilai N, She L, Liu BQ, Vuguin P, Cohen P, Wang J, Rossetti L. Surgical removal of visceral fat reverses hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes 48: 94–98, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Basu R, Breda E, Oberg AL, Powell CC, Dalla Man C, Basu A, Vittone JL, Klee GG, Arora P, Jensen MD, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Rizza RA. Mechanisms of the age-associated deterioration in glucose tolerance: contribution of alterations in insulin secretion, action, and clearance. Diabetes 52: 1738–1748, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

