A role for topoisomerase II alpha in the formation of radiation-induced chromatid breaks
- PMID: 18665175
- PMCID: PMC2527830
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604514
A role for topoisomerase II alpha in the formation of radiation-induced chromatid breaks
Abstract
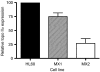
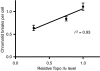
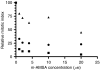
Chromatid breaks in cells exposed to low dose irradiation are thought to be initiated by DNA double-strand breaks (DSB), and the frequency of chromatid breaks has been shown to increase in DSB rejoining deficient cells. However, the underlying causes of the wide variation in frequencies of G2 chromatid breaks (or chromatid 'radiosensitivity') in irradiated T-lymphocytes from different normal individuals and cancer cases are as yet unclear. Here we report evidence that topoisomerase II alpha expression level is a factor determining chromatid radiosensitivity. We have exposed the promyelocytic leukaemic cell line (HL60) and two derived variant cell lines (MX1 and MX2) that have acquired resistance to mitoxantrone and low expression of topoisomerase II alpha, to low doses of gamma-radiation and scored the induced chromatid breaks. Chromatid break frequencies were found to be significantly lower in the variant cell lines, compared with their parental HL60 cell line. Rejoining of DSB in the variant cell lines was similar to that in the parental HL60 strain. Our results indicate the indirect involvement of topoisomerase II alpha in the formation of radiation-induced chromatid breaks from DSB, and suggest topoisomerase II alpha as a possible factor in the inter-individual variation in chromatid radiosensitivity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of the formation of radiation-induced chromosomal aberrations.Mutat Res. 2010 Aug 14;701(1):23-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.03.016. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20348019 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of topoisomerase IIalpha expression and function in human cells decreases chromosomal radiosensitivity.Mutat Res. 2009 Apr 26;663(1-2):40-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.01.003. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Mutat Res. 2009. PMID: 19428368 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase II is required for mitoxantrone to signal nuclear factor kappa B activation in HL60 cells.J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 18;275(33):25231-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.33.25231. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10940316
-
Progress towards understanding the nature of chromatid breakage.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;104(1-4):65-71. doi: 10.1159/000077467. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15162016 Review.
-
G2 chromatid aberrations: kinetics and possible mechanisms.Environ Mol Mutagen. 1993;22(4):250-6. doi: 10.1002/em.2850220412. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1993. PMID: 8223506 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of the formation of radiation-induced chromosomal aberrations.Mutat Res. 2010 Aug 14;701(1):23-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.03.016. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20348019 Free PMC article.
-
Radioresistance in a human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell line is associated with DNA methylation changes and topoisomerase II α.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(4):558-66. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1017154. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25719218 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of topoisomerase IIalpha expression and function in human cells decreases chromosomal radiosensitivity.Mutat Res. 2009 Apr 26;663(1-2):40-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.01.003. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Mutat Res. 2009. PMID: 19428368 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoporin 54 contributes to homologous recombination repair and post-replicative DNA integrity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 6;46(15):7731-7746. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky569. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29986057 Free PMC article.
-
TOP2A correlates with poor prognosis and affects radioresistance of medulloblastoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 15;12:918959. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.918959. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35912241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin CA, Marsh KL (1998) Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase II beta. Bioessays 20: 215–226 - PubMed
-
- Baeyens A, Broecke RVD, Makar A, Thierens H, de Ridder L, Vral A (2005) Chromosomal radiosensitivity in breast cancer patients: Influence of age of onset of the disease. Oncol Rep 13: 347–353 - PubMed
-
- Baria K, Warren C, Eden OB, Roberts SA, West CM, Scott D (2002) Chromosomal radiosensitivity in young cancer patients: possible evidence of genetic predisposition. Int J Radiat Biol 78: 341–346 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

