Design and construction of a double inversion recombination switch for heritable sequential genetic memory
- PMID: 18665232
- PMCID: PMC2481393
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002815
Design and construction of a double inversion recombination switch for heritable sequential genetic memory
Abstract
Background: Inversion recombination elements present unique opportunities for computing and information encoding in biological systems. They provide distinct binary states that are encoded into the DNA sequence itself, allowing us to overcome limitations posed by other biological memory or logic gate systems. Further, it is in theory possible to create complex sequential logics by careful positioning of recombinase recognition sites in the sequence.
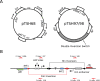
Methodology/principal findings: In this work, we describe the design and synthesis of an inversion switch using the fim and hin inversion recombination systems to create a heritable sequential memory switch. We have integrated the two inversion systems in an overlapping manner, creating a switch that can have multiple states. The switch is capable of transitioning from state to state in a manner analogous to a finite state machine, while encoding the state information into DNA. This switch does not require protein expression to maintain its state, and "remembers" its state even upon cell death. We were able to demonstrate transition into three out of the five possible states showing the feasibility of such a switch.
Conclusions/significance: We demonstrate that a heritable memory system that encodes its state into DNA is possible, and that inversion recombination system could be a starting point for more complex memory circuits. Although the circuit did not fully behave as expected, we showed that a multi-state, temporal memory is achievable.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Day A, Cole H, Doan K, Fuller K, Liang S, et al. BactoBlood 2007
-
- Gardner TS, Cantor CR, Collins JJ. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature. 2000;403:339–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

