Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing
- PMID: 18665274
- PMCID: PMC2475661
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002836
Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing
Abstract
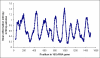
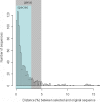
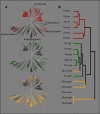
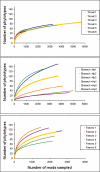
Humans host complex microbial communities believed to contribute to health maintenance and, when in imbalance, to the development of diseases. Determining the microbial composition in patients and healthy controls may thus provide novel therapeutic targets. For this purpose, high-throughput, cost-effective methods for microbiota characterization are needed. We have employed 454-pyrosequencing of a hyper-variable region of the 16S rRNA gene in combination with sample-specific barcode sequences which enables parallel in-depth analysis of hundreds of samples with limited sample processing. In silico modeling demonstrated that the method correctly describes microbial communities down to phylotypes below the genus level. Here we applied the technique to analyze microbial communities in throat, stomach and fecal samples. Our results demonstrate the applicability of barcoded pyrosequencing as a high-throughput method for comparative microbial ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Savage DC. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. - PubMed
-
- Wostmann BS, Larkin C, Moriarty A, Bruckner-Kardoss E. Dietary intake, energy metabolism, and excretory losses of adult male germfree Wistar rats. Lab Anim Sci. 1983;33:46–50. - PubMed
-
- Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006;444:1027–1031. - PubMed
-
- Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 2004;118:229–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

