Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors and pathogenesis
- PMID: 18666317
- PMCID: PMC2731180
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.4300
Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors and pathogenesis
Abstract
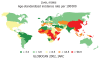
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the commonest primary malignant cancer of the liver in the world. Given that the burden of chronic liver disease is expected to rise owing to increasing rates of alcoholism, hepatitis B and C prevalence and obesity-related fatty liver disease, it is expected that the incidence of HCC will also increase in the foreseeable future. This article summarizes the international epidemiology, the risk factors and the pathogenesis of HCC, including the roles of viral hepatitis, toxins, such as alcohol and aflatoxin, and insulin resistance.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Mortality database. Available from: URL: http://www.who.int/whosis/en.
-
- Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of 25 major cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer. 1999;80:827–841. - PubMed
-
- Montalto G, Cervello M, Giannitrapani L, Dantona F, Terranova A, Castagnetta LA. Epidemiology, risk factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;963:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Sherman M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin Liver Dis. 2005;25:143–154. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical