A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee
- PMID: 18667054
- PMCID: PMC2575633
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2461
A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee
Abstract
Introduction: 5-Loxin is a novel Boswellia serrata extract enriched with 30% 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA), which exhibits potential anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the 5-lipoxygenase enzyme. A 90-day, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee.
Methods: Seventy-five OA patients were included in the study. The patients received either 100 mg (n = 25) or 250 mg (n = 25) of 5-Loxin daily or a placebo (n = 25) for 90 days. Each patient was evaluated for pain and physical functions by using the standard tools (visual analog scale, Lequesne's Functional Index, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) at the baseline (day 0), and at days 7, 30, 60 and 90. Additionally, the cartilage degrading enzyme matrix metalloproteinase-3 was also evaluated in synovial fluid from OA patients. Measurement of a battery of biochemical parameters in serum and haematological parameters, and urine analysis were performed to evaluate the safety of 5-Loxin in OA patients.
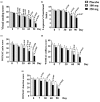
Results: Seventy patients completed the study. At the end of the study, both doses of 5-Loxin conferred clinically and statistically significant improvements in pain scores and physical function scores in OA patients. Interestingly, significant improvements in pain score and functional ability were recorded in the treatment group supplemented with 250 mg 5-Loxin as early as 7 days after the start of treatment. Corroborating the improvements in pain scores in treatment groups, we also noted significant reduction in synovial fluid matrix metalloproteinase-3. In comparison with placebo, the safety parameters were almost unchanged in the treatment groups.
Conclusion: 5-Loxin reduces pain and improves physical functioning significantly in OA patients; and it is safe for human consumption. 5-Loxin may exert its beneficial effects by controlling inflammatory responses through reducing proinflammatory modulators, and it may improve joint health by reducing the enzymatic degradation of cartilage in OA patients.
Trial registration: (
Clinical trial registration number: ISRCTN05212803.).
Figures
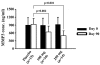
Comment in
-
Lipooxygenase inhibition in osteoarthritis: a potential symptomatic and disease modifying effect?Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(5):116. doi: 10.1186/ar2490. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18828886 Free PMC article.
-
A new 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor seems to be safe and effective for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009 Mar;5(3):132-3. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum1006. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19190622
Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin and AflapinAgainst osteoarthritis of the knee: a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study.Int J Med Sci. 2010 Nov 1;7(6):366-77. doi: 10.7150/ijms.7.366. Int J Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 21060724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study evaluates the early efficacy of aflapin in subjects with osteoarthritis of knee.Int J Med Sci. 2011;8(7):615-22. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8.615. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Int J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22022214 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Aflapin®, a Novel Boswellia Serrata Extract, in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Short-Term 30-Day Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study.J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Feb;42(2):159-168. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2021.2014370. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 35512759 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of Boswellia and Boswellia extract for osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jul 17;20(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02985-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32680575 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Extracts of Oleogum Resin of Boswellia in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Phytother Res. 2024 Dec;38(12):5672-5689. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8336. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 39314013 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cancer Chemopreventive Effects of Boswellia sacra Gum Resin Hydrodistillates on Invasive Urothelial Cell Carcinoma: Report of a Case.Integr Cancer Ther. 2017 Dec;16(4):605-611. doi: 10.1177/1534735416664174. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Integr Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 27531547 Free PMC article.
-
An Anti-Inflammatory Composition of Boswellia serrata Resin Extracts Alleviates Pain and Protects Cartilage in Monoiodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 May 21;2020:7381625. doi: 10.1155/2020/7381625. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32565872 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of adverse radiation effects with Boswellia serrata after failure of pentoxifylline and vitamin E: illustrative cases.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2023 Jan 30;5(5):CASE22488. doi: 10.3171/CASE22488. Print 2023 Jan 30. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2023. PMID: 36718863 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid attenuates titanium particle-induced osteogenic inhibition via activation of the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Theranostics. 2019 Sep 23;9(24):7140-7155. doi: 10.7150/thno.35988. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31695758 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a novel Boswellia serrata extract in the management of osteoarthritis of the knee.Phytother Res. 2019 May;33(5):1457-1468. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6338. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30838706 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA, Hirsch R, Helmick CG, Jordan JM, Kington RS, Lane NE, Nevitt MC, Zhang Y, Sowers M, McAlindon T, Spector TD, Poole AR, Yanovski SZ, Ateshian G, Sharma L, Buckwalter JA, Brandt KD, Fries JF. Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann Intern Med. 2000;133:635–646. - PubMed
-
- Hochberg MC, Altman RD, Brandt KD, Clark BM, Dieppe PA, Griffin MR, Moskowitz RW, Schnitzer TJ. Guidelines for the medical management of osteoarthritis. Part II. Osteoarthritis of the knee. American College of Rheumatology. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1541–1546. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381104. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

