Coordinated actions of the forkhead protein Foxp1 and Hox proteins in the columnar organization of spinal motor neurons
- PMID: 18667151
- PMCID: PMC2547125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.025
Coordinated actions of the forkhead protein Foxp1 and Hox proteins in the columnar organization of spinal motor neurons
Abstract
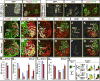
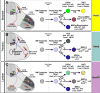
The formation of locomotor circuits depends on the spatially organized generation of motor columns that innervate distinct muscle and autonomic nervous system targets along the body axis. Within each spinal segment, multiple motor neuron classes arise from a common progenitor population; however, the mechanisms underlying their diversification remain poorly understood. Here, we show that the Forkhead domain transcription factor Foxp1 plays a critical role in defining the columnar identity of motor neurons at each axial position. Using genetic manipulations, we demonstrate that Foxp1 establishes the pattern of LIM-HD protein expression and accordingly organizes motor axon projections, their connectivity with peripheral targets, and the establishment of motor pools. These functions of Foxp1 act in accordance with the rostrocaudal pattern provided by Hox proteins along the length of the spinal cord, suggesting a model by which motor neuron diversity is achieved through the coordinated actions of Foxp1 and Hox proteins.
Figures






References
-
- Arber S, Han B, Mendelsohn M, Smith M, Jessell TM, Sockanathan S. Requirement for the homeobox gene Hb9 in the consolidation of motor neuron identity. Neuron. 1999;23:659–674. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Ladle DR, Lin JH, Frank E, Jessell TM. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell. 2000;101:485–498. - PubMed
-
- Butler SJ, Tear G. Getting axons onto the right path: the role of transcription factors in axon guidance. Development. 2007;134:439–448. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter EM, Goddard JM, Davis AP, Nguyen TP, Capecchi MR. Targeted disruption of Hoxd-10 affects mouse hindlimb development. Development. 1997;124:4505–4514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

