Down-regulation of transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation and inflammation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring
- PMID: 18667178
- PMCID: PMC2597035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.05.022
Down-regulation of transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation and inflammation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring
Abstract
Objective: Intrauterine growth-restricted (IUGR) newborns have increased risk of obesity-induced fatty liver and inflammation. We hypothesized that IUGR-induced inhibition of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) is associated with an increased inflammatory response.
Study design: Rat control dams received ad libitum food, whereas study dams were 50% food restricted from pregnancy day 10 to 21 (IUGR). Pups were nursed by control dams and weaned to ad libitum feed. Hepatic protein expression of transcription factors, lipid enzymes, triglyceride content, and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were analyzed in 1 day and 9 month old male offspring.
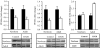
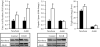
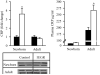
Results: At 1 day of age, IUGR pups showed down-regulation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma and up-regulation of hepatic lipase and CRP. At 9 months of age, IUGR exhibited continued down-regulation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma with up-regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 and fatty acid synthase. Furthermore, IUGR adults had increased hepatic triglyceride content and plasma CRP levels.
Conclusions: The results suggest that developmental hepatic dysregulation may contribute to programmed obesity-induced inflammation in IUGR offspring.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gender-specific programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007 May;196(5):477.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.02.024. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007. PMID: 17466711
-
Correlations of PPARα and PPARγ expressions with 1H-MRS quantified hepatic fat content in pups of rats that experienced intrauterine growth restriction.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021 Feb;34(4):606-613. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2019.1611766. Epub 2019 May 8. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021. PMID: 31068026
-
Prenatal ethanol exposure programs an increased susceptibility of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in female adult offspring rats.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 15;274(2):263-73. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.11.009. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24275070
-
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPAR), fatty acids and microRNAs: Implications in women delivering low birth weight babies.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2021 Feb;67(1):24-41. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2020.1858994. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2021. PMID: 33719831 Review.
-
Fetal programming of adipose tissue: effects of intrauterine growth restriction and maternal obesity/high-fat diet.Semin Reprod Med. 2011 May;29(3):237-45. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1275517. Epub 2011 Jun 27. Semin Reprod Med. 2011. PMID: 21710399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of placental insufficiency and intrauterine growth restriction on the activation of fetal hepatic glucose production.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016 Nov 5;435:61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.12.016. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26723529 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms governing offspring metabolic programming in rodent models of in utero stress.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Dec;77(23):4861-4898. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03566-z. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32494846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Dysregulation Associate with Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Species and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine in Low-Birth-Weight Goats.Animals (Basel). 2022 Mar 18;12(6):766. doi: 10.3390/ani12060766. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327163 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemistry, hormones and adipocytokines in prepubertal children born with IUGR evoke metabolic, hepatic and renal derangements.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 24;8(1):15691. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34075-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30356143 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosine methylation dysregulation in neonates following intrauterine growth restriction.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 26;5(1):e8887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008887. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20126273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desai M, Babu J, Ross MG. Programmed metabolic syndrome: prenatal undernutrition and postweaning overnutrition. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;293:R2306–14. - PubMed
-
- Roberts A, Nava S, Bocconi L, Salmona S, Nicolini U. Liver function tests and glucose and lipid metabolism in growth-restricted fetuses. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;94:290–4. - PubMed
-
- Leclercq IA. Pathogenesis of steatohepatitis: insights from the study of animal models. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007;70:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury MW. Lipid Metabolism and Liver Inflammation. I. Hepatic fatty acid uptake: possible role in steatosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G194–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

