Down-regulation of transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation and inflammation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring
- PMID: 18667178
- PMCID: PMC2597035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.05.022
Down-regulation of transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation and inflammation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring
Abstract
Objective: Intrauterine growth-restricted (IUGR) newborns have increased risk of obesity-induced fatty liver and inflammation. We hypothesized that IUGR-induced inhibition of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) is associated with an increased inflammatory response.
Study design: Rat control dams received ad libitum food, whereas study dams were 50% food restricted from pregnancy day 10 to 21 (IUGR). Pups were nursed by control dams and weaned to ad libitum feed. Hepatic protein expression of transcription factors, lipid enzymes, triglyceride content, and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were analyzed in 1 day and 9 month old male offspring.
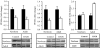
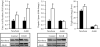
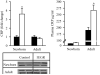
Results: At 1 day of age, IUGR pups showed down-regulation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma and up-regulation of hepatic lipase and CRP. At 9 months of age, IUGR exhibited continued down-regulation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma with up-regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 and fatty acid synthase. Furthermore, IUGR adults had increased hepatic triglyceride content and plasma CRP levels.
Conclusions: The results suggest that developmental hepatic dysregulation may contribute to programmed obesity-induced inflammation in IUGR offspring.
Figures
References
-
- Desai M, Babu J, Ross MG. Programmed metabolic syndrome: prenatal undernutrition and postweaning overnutrition. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;293:R2306–14. - PubMed
-
- Roberts A, Nava S, Bocconi L, Salmona S, Nicolini U. Liver function tests and glucose and lipid metabolism in growth-restricted fetuses. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;94:290–4. - PubMed
-
- Leclercq IA. Pathogenesis of steatohepatitis: insights from the study of animal models. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007;70:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury MW. Lipid Metabolism and Liver Inflammation. I. Hepatic fatty acid uptake: possible role in steatosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G194–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

