Investigation of the ionisation density dependence of the glow curve characteristics of LIF:MG,TI (TLD-100)
- PMID: 18667402
- PMCID: PMC3480322
- DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncn197
Investigation of the ionisation density dependence of the glow curve characteristics of LIF:MG,TI (TLD-100)
Abstract
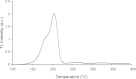
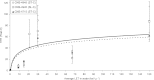
The dependence of the shape of the glow curve of LiF:Mg,Ti (TLD-100) on ionisation density was investigated using irradiation with (90)Sr/(90)Y beta rays, 60 and 250 kVp X rays, various heavy-charged particles and 0.2 and 14 MeV neutrons. Special attention is focused on the properties of high-temperature thermoluminescence; specifically, the behaviour of the high-temperature ratio (HTR) of Peaks 7 and 8 as a function of batch and annealing protocol. The correlation of Peaks 7 and 8 with average linear-energy-transfer (LET) is also investigated. The HTR of Peak 7 is found to be independent of LET for values of LET approximately >30 keV microm(-1). The behaviour of the HTR of Peak 8 with LET is observed to be erratic, which suggests that applications using the HTR should separate the contributions of Peaks 7 and 8 using computerised glow curve deconvolution. The behaviour of the HTR following neutron irradiation is complex and not fully understood. The shape of composite Peak 5 is observed to be broader following high ionisation alpha particle irradiation, suggesting that the combined use of the HTR and the shape of Peak 5 could lead to improved ionisation density discrimination for particles of high LET.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effects of ionisation density on the glow curve structure of LiF:Mg,Ti (TLD-100): the behaviour of composite glow peak 5 in 'slow-cooled' material.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007;126(1-4):194-7. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncm041. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. PMID: 17562651
-
Advanced multistage deconvolution applied to composite glow peak 5 in LiF:Mg,Ti (TLD-100).Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007;126(1-4):322-5. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncm067. Epub 2007 May 20. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. PMID: 17517677
-
Pre- and post-irradiation fading of 6LiF:Mg,Ti (TLD-600) exposed to thermal neutrons.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007;126(1-4):318-21. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncm066. Epub 2007 May 12. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. PMID: 17496295
-
The application of LiF:Mg,Cu,P to large scale personnel dosimetry: current status and future directions.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2006;119(1-4):248-54. doi: 10.1093/rpd/nci692. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2006. PMID: 16835277 Review.
-
On the use of LiF:Mg,Ti thermoluminescence dosemeters in space--a critical review.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2003;106(1):7-24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a006337. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2003. PMID: 14653322 Review.
Cited by
-
50 Years of the Radiological Research Accelerator Facility (RARAF).Radiat Res. 2017 Apr;187(4):413-423. doi: 10.1667/RR002CC.1. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Radiat Res. 2017. PMID: 28140790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horowitz Y. S. Theory of thermoluminescence gamma dose response: the unified inter-action model. Nucl. Instrum. Meths. 2001;B184:68–84.
-
- Olko P., Bilski P., Kim J. L. Microdosimetric interpretation of the photon energy response of LiF:Mg,Ti detectors. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2002;100:119–122. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz Y. S., Avila O., Rodriguez-Villafuerte M. Theory of heavy charged particle (efficiency and supralinearity) in TL materials. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B. 2001;184:85–122.
-
- Julius H. W., de Planque G. Influence of annealing and readout procedures on fading and sensitivity changes in LiF for temperatures and humidities typical for environmental and personnel dosimetry. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1983;6:253–256.
-
- Uray I. Dose independent use of LiF detectors in neutron-gamma radiation fields. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1986;17:127–129.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

