GammadeltaT cells initiate acute inflammation and injury in adenovirus-infected liver via cytokine-chemokine cross talk
- PMID: 18667515
- PMCID: PMC2546965
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00927-08
GammadeltaT cells initiate acute inflammation and injury in adenovirus-infected liver via cytokine-chemokine cross talk
Abstract
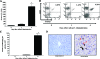
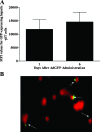
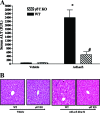
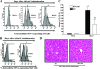
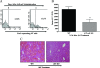
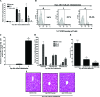
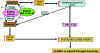
Emerging studies suggest an important role for the innate immune response in replication-defective adenovirus (Ad)-mediated acute liver toxicity. Specifically, classical innate immune cells (including NK cells, neutrophils, and Kupffer cells) have all been implicated in the development of Ad-mediated acute liver toxicity. The nonclassical innate immune T cell, the gammadeltaT cell, has been implicated in the pathophysiology of several viral infections that predominantly affect the mucosa and brain, but the specific role in the pathology of AdLacZ-mediated acute liver inflammation and injury as well as accompanying vector clearance is largely unknown. In the present study, we demonstrated that a CXCL9-CXCR3-dependent mechanism governed the accumulation of gammadeltaT cells in the livers of mice infected with Ad expressing the Escherichia coli LacZ gene (AdLacZ). We also showed a critical role for gammadeltaT cells in initiating acute liver toxicity after AdLacZ administration, driven in part by the ability of gammadeltaT cells to promote the recruitment of the conventional T cell, the CD8(+) T cell, into the liver. Furthermore, reduced hepatic injury in AdLacZ-infected gammadeltaT-cell-deficient mice was associated with lower hepatic levels of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and CXCL9, an IFN-gamma-inducible chemokine. Finally, our study highlighted a key role for IFN-gamma and CXCL9 cross talk acting in a feedback loop to drive the proinflammatory effects of gammadeltaT cells during AdLacZ-mediated acute liver toxicity. Specifically, intracellular IFN-gamma produced by activated hepatic gammadeltaT cells interacts with hepatocytes to mediate hepatic CXCL9 production, with the consequent accumulation of CXCR3-bearing gammadeltaT cells in the liver to cause acute liver damage without vector clearance.
Figures
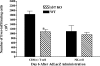
References
-
- Ajuebor, M. N., A. I. Aspinall, F. Zhou, T. Le, Y. Yang, S. J. Urbanski, S. Sidobre, M. Kronenberg, C. M. Hogaboam, and M. G. Swain. 2005. Lack of chemokine receptor CCR5 promotes murine fulminant liver failure by preventing the apoptosis of activated CD1d-restricted NKT cells. J. Immunol. 1748027-8037. - PubMed
-
- Ajuebor, M. N., C. M. Hogaboam, T. Le, A. E. Proudfoot, and M. G. Swain. 2004. CCL3/MIP-1α is pro-inflammatory in murine T cell-mediated hepatitis by recruiting CCR1-expressing CD4+ T cells to the liver. Eur. J. Immunol. 342907. - PubMed
-
- Ajuebor, M. N., C. M. Hogaboam, T. Le, and M. G. Swain. 2003. C-C chemokine ligand 2/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 directly inhibits NKT cell IL-4 production and is hepatoprotective in T cell-mediated hepatitis in the mouse. J. Immunol. 1705252-5259. - PubMed
-
- Ajuebor, M. N., M. G. Swain, and M. Perretti. 2002. Chemokines as novel therapeutic targets in inflammatory diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 631191-1196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

